COVID-19 pneumonia in lung transplant recipients: understanding risk factors and treatment outcomes in Japan
- PMID: 38856777
- PMCID: PMC11164722
- DOI: 10.1007/s10238-024-01388-y
COVID-19 pneumonia in lung transplant recipients: understanding risk factors and treatment outcomes in Japan
Abstract
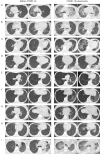
Lung transplant (LTx) recipients face a significant risk from coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19), with elevated hospitalization mortality rates even post-vaccination. While severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) typically induces pneumonia in even healthy individuals, it can also infect the transplanted lungs of LTx recipients, potentially leading to graft dysfunction. Despite the prevalence of COVID-19 pneumonia in LTx recipients, data on its characteristics and associated risk factors remain limited. This retrospective study analyzed data from LTx recipients at Tohoku University Hospital between January 2001 and November 2023. COVID-19 cases were identified, and patient records, including thoracic computed tomography (CT) evaluations, were reviewed. Patient characteristics, vaccination history, immunosuppressant use, and comorbidities were assessed. Descriptive analysis was utilized for data presentation. Among 172 LTx recipients, 39 (22.7%) contracted COVID-19, with 9 (23%) developing COVID-19 pneumonia. COVID-19 incidence in LTx recipients aligned with national rates, but pneumonia risk was elevated. Delayed antiviral therapy initiation was noted in pneumonia cases. Remdesivir was uniformly administered and remained the primary treatment choice. LTx recipients are susceptible to COVID-19 pneumonia, warranting vigilance and tailored management strategies. Pre-transplant vaccination and prompt COVID-19 diagnosis and treatment are imperative for optimizing outcomes in this population.
Keywords: COVID-19; Japan; Lung transplant; Pneumonia; Remdesivir; SARS-CoV-2; Vaccine.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Agrawal U, Bedston S, McCowan C, Oke J, Patterson L, Robertson C, et al. Severe COVID-19 outcomes after full vaccination of primary schedule and initial boosters: pooled analysis of national prospective cohort studies of 30 million individuals in England, Northern Ireland, Scotland, and wales. Lancet. 2022;400:1305–20. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

