Disseminated septic arthritis caused by Ureaplasma urealyticum in an immunocompromised patient with hypogammaglobulinemia after rituximab therapy
- PMID: 38856807
- PMCID: PMC11621129
- DOI: 10.1007/s15010-024-02301-1
Disseminated septic arthritis caused by Ureaplasma urealyticum in an immunocompromised patient with hypogammaglobulinemia after rituximab therapy
Abstract
Purpose: Ureaplasma urealyticum is a rare pathogen associated with septic arthritis that predominantly affects patients with hypogammaglobulinemia. Bacterial identification of fastidious organisms is challenging because they are undetectable by routine culture testing. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first report of septic arthritis induced by U. urealyticum infection in Japan.
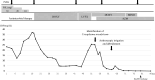
Case description: We describe the case of a 23-year-old Japanese female with secondary hypogammaglobulinemia (serum immunoglobulin level < 500 mg/dL), identified 8 years after treatment with rituximab. The patient presented with persistent fever and polyarthritis that were unresponsive to ceftriaxone and prednisolone. Contrast-enhanced computed tomography and gallium-67 scintigraphy revealed effusion and inflammation in the left sternoclavicular, hip, wrist, knee, and ankle joints. Although Gram staining and bacterial culture of the drainage fluid from the left hip joint were negative, the condition exhibited characteristics of purulent bacterial infection. The patient underwent empirical treatment with doxycycline, and her symptoms promptly resolved. Subsequent 16S ribosomal RNA (rRNA) gene sequencing of the joint fluid confirmed the presence of U. urealyticum, leading to the diagnosis of septic arthritis. Combination therapy with doxycycline and azithromycin yielded a favorable recovery from the inflammatory status and severe arthritic pain.
Conclusion: This case highlights U. urealyticum as a potential causative agent of disseminated septic arthritis, particularly in patients with hypogammaglobulinaemia. The 16S rRNA gene analysis proved beneficial for identifying pathogens in culture-negative specimens, such as synovial fluid, in suspected bacterial infections.
Keywords: Ureaplasma urealyticum; 16S rRNA gene sequencing; Hypogammaglobulinemia; Joint infection; Rituximab; α-Defensin.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Conflict of interest: The authors have no conflicts of interest. Consent for publication: Written informed consent for publication was obtained from the patient.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Septic arthritis of the shoulder due to Ureaplasma urealyticum after emergency caesarean section: a case report.BMC Infect Dis. 2020 Oct 17;20(1):767. doi: 10.1186/s12879-020-05497-3. BMC Infect Dis. 2020. PMID: 33069221 Free PMC article.
-
Ureaplasma urealyticum septic oligoarthritis in a patient with severe secondary hypogammaglobulinaemia.Med J Aust. 2021 Jun;214(11):506-507.e1. doi: 10.5694/mja2.51107. Epub 2021 May 27. Med J Aust. 2021. PMID: 34046899 No abstract available.
-
Ureaplasma urealyticum disseminated multifocal abscesses in an immunocompromised adult patient: a case report.BMC Infect Dis. 2020 Jan 15;20(1):47. doi: 10.1186/s12879-020-4771-z. BMC Infect Dis. 2020. PMID: 31941460 Free PMC article.
-
Rare case of Ureaplasma parvum septic arthritis in an immunocompetent patient.BMJ Case Rep. 2020 Sep 8;13(9):e236396. doi: 10.1136/bcr-2020-236396. BMJ Case Rep. 2020. PMID: 32907868 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Efficacy of azithromycin in treating Ureaplasma urealyticum: a systematic review and meta-analysis.BMC Infect Dis. 2023 Mar 16;23(1):163. doi: 10.1186/s12879-023-08102-5. BMC Infect Dis. 2023. PMID: 36927441 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Prior immunity to Ureaplasma urealyticum protects against respiratory infection in immunosuppressed mice.Microbiol Spectr. 2025 Jan 7;13(1):e0176324. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.01763-24. Epub 2024 Nov 19. Microbiol Spectr. 2025. PMID: 39560424 Free PMC article.
-
Disseminated Ureaplasma urealyticum Infection and Hyperammonemic Encephalopathy in a Patient With Activated PI3K Delta Syndrome 2.Open Forum Infect Dis. 2025 Feb 17;12(2):ofaf084. doi: 10.1093/ofid/ofaf084. eCollection 2025 Feb. Open Forum Infect Dis. 2025. PMID: 40041443 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Capoccia R, Greub G, Baud D. Ureaplasma urealyticum, Mycoplasma hominis and adverse pregnancy outcomes. Curr Opin Infect Dis. 2013;26:231–40. - PubMed
-
- Wang QY, Li RH, Zheng LQ, Shang XH. Prevalence and antimicrobial susceptibility of Ureaplasma urealyticum and Mycoplasma hominis in female outpatients, 2009–2013. J Microbiol Immunol Infect. 2016;49:359–62. - PubMed
-
- Kokkayil P, Dhawan B. Ureaplasma: current perspectives. Indian J Med Microbiol. 2015;33:205–14. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

