Inflammatory diseases causing joint and bone destruction: rheumatoid arthritis and hemophilic arthropathy
- PMID: 38856919
- PMCID: PMC11415468
- DOI: 10.1007/s00774-024-01520-8
Inflammatory diseases causing joint and bone destruction: rheumatoid arthritis and hemophilic arthropathy
Abstract
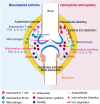
Various diseases and conditions cause joint disorders. Osteoarthritis (OA) is characterized by the degeneration of articular cartilage, synovitis, and anabolic changes in surrounding bone tissues. In contrast, rheumatoid arthritis (RA) and hemophilic arthropathy (HA) display marked destruction of bone tissues caused by synovitis. RA is a representative autoimmune disease. The primary tissue of RA pathogenesis is the synovial membrane and involves various immune cells that produce catabolic cytokines and enzymes. Hemophilia is a genetic disorder caused by a deficiency in blood clotting factors. Recurrent intra-articular bleeding leads to chronic synovitis through excessive iron deposition and results in the destruction of affected joints. Although the triggers for these two joint diseases are completely different, many cytokines and enzymes are common in the pathogenesis of both RA and HA. This review focuses on the similarities between joint and bone destruction in RA and HA. The insights may be useful in developing better treatments for hemophilia patients with arthropathy and osteoporosis by leveraging advanced therapeutics for RA.
Keywords: Hemophilia; Hemophilic arthropathy; Joint destruction; Rheumatoid arthritis.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Blood-induced joint disease: the pathophysiology of hemophilic arthropathy.J Thromb Haemost. 2010 Sep;8(9):1895-902. doi: 10.1111/j.1538-7836.2010.03962.x. J Thromb Haemost. 2010. PMID: 20586922 Review.
-
Cytokines in the pathogenesis of hemophilic arthropathy.Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2018 Feb;39:71-91. doi: 10.1016/j.cytogfr.2017.11.003. Epub 2017 Nov 13. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2018. PMID: 29153709 Review.
-
Blood-induced arthropathy in hemophilia: mechanisms and heterogeneity.Semin Thromb Hemost. 2015 Nov;41(8):832-7. doi: 10.1055/s-0035-1564445. Epub 2015 Oct 9. Semin Thromb Hemost. 2015. PMID: 26451745 Review.
-
Pathogenesis of hemophilic arthropathy.Semin Hematol. 2006 Jan;43(1 Suppl 1):S18-22. doi: 10.1053/j.seminhematol.2005.11.026. Semin Hematol. 2006. PMID: 16427379 Review.
-
Biomarkers Involved in the Pathogenesis of Hemophilic Arthropathy.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Sep 13;25(18):9897. doi: 10.3390/ijms25189897. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39337384 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Belt Electrode-Skeletal Muscle Electrical Stimulation Prevents Muscle Atrophy in the Soleus of Collagen-Induced Arthritis Rats.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Apr 2;26(7):3294. doi: 10.3390/ijms26073294. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40244146 Free PMC article.
-
Decision experiences in joint replacement surgery for patients with haemophilic arthritis: A qualitative study.BMC Med Inform Decis Mak. 2025 Feb 4;25(1):55. doi: 10.1186/s12911-025-02901-3. BMC Med Inform Decis Mak. 2025. PMID: 39905363 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Smolen JS, Aletaha D, Barton A, Burmester GR, Emery P, Firestein GS, Kavanaugh A, McInnes IB, Solomon DH, Strand V, Yamamoto K (2018) Rheumatoid arthritis. Nat Rev Dis Primers 4:18001. 10.1038/nrdp.2018.1 - PubMed
-
- Valentino L (2010) Blood-induced joint disease: the pathophysiology of hemophilic arthropathy. J Thromb Haemost 8:1895–1902 - PubMed
-
- Safiri S, Kolahi AA, Hoy D, Smith E, Bettampadi D, Mansournia MA, Almasi-Hashiani A, Ashrafi-Asgarabad A, Moradi-Lakeh M, Qorbani M, Collins G, Woolf AD, March L, Cross M (2019) Global, regional and national burden of rheumatoid arthritis 1990–2017: a systematic analysis of the global burden of disease study 2017. Ann Rheum Dis 78:1463–1471. 10.1136/annrheumdis-2019-215920 - PubMed
-
- Nakajima A, Sakai R, Inoue E, Harigai M (2020) Prevalence of patients with rheumatoid arthritis and age-stratified trends in clinical characteristics and treatment, based on the national database of health insurance claims and specific health checkups of Japan. Int J Rheum Dis 23:1676–1684 - PubMed
-
- Kojima M, Nakayama T, Tsutani K, Igarashi A, Kojima T, Suzuki S, Miyasaka N, Yamanaka H (2020) Epidemiological characteristics of rheumatoid arthritis in Japan: prevalence estimates using a nationwide population-based questionnaire survey. Mod Rheumatol 30:941–947. 10.1080/14397595.2019.1682776 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

