A Bibliometric Analysis of the Spatial Transcriptomics Literature from 2006 to 2023
- PMID: 38856921
- PMCID: PMC11164738
- DOI: 10.1007/s10571-024-01484-3
A Bibliometric Analysis of the Spatial Transcriptomics Literature from 2006 to 2023
Abstract
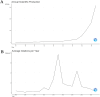
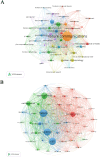
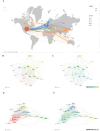
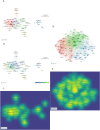
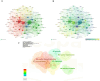
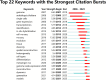
In recent years, spatial transcriptomics (ST) research has become a popular field of study and has shown great potential in medicine. However, there are few bibliometric analyses in this field. Thus, in this study, we aimed to find and analyze the frontiers and trends of this medical research field based on the available literature. A computerized search was applied to the WoSCC (Web of Science Core Collection) Database for literature published from 2006 to 2023. Complete records of all literature and cited references were extracted and screened. The bibliometric analysis and visualization were performed using CiteSpace, VOSviewer, Bibliometrix R Package software, and Scimago Graphica. A total of 1467 papers and reviews were included. The analysis revealed that the ST publication and citation results have shown a rapid upward trend over the last 3 years. Nature Communications and Nature were the most productive and most co-cited journals, respectively. In the comprehensive global collaborative network, the United States is the country with the most organizations and publications, followed closely by China and the United Kingdom. The author Joakim Lundeberg published the most cited paper, while Patrik L. Ståhl ranked first among co-cited authors. The hot topics in ST are tissue recognition, cancer, heterogeneity, immunotherapy, differentiation, and models. ST technologies have greatly contributed to in-depth research in medical fields such as oncology and neuroscience, opening up new possibilities for the diagnosis and treatment of diseases. Moreover, artificial intelligence and big data drive additional development in ST fields.
Keywords: Bibliometric analysis; Cancer; Differentiation; Models; Spatial transcriptomics; Tissue recognition.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Al-Sabah J, Baccin C, Haas S (2019) Single-cell and spatial transcriptomics approaches of the bone marrow microenvironment. Curr Opin Oncol 32(2):146–153 - PubMed
-
- Aria M, Cuccurullo C (2017) bibliometrix: an R-tool for comprehensive science mapping analysis. J Informet 11(4):959–975. 10.1016/j.joi.2017.08.007
-
- Bao Z, Wang Y, Wang Q, Fang S, Shan X, Wang J, Jiang T (2021) Intratumor heterogeneity, microenvironment, and mechanisms of drug resistance in glioma recurrence and evolution. Front Med 15(4):551–561. 10.1007/s11684-020-0760-2 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

