Global Prevalence of Overweight and Obesity in Children and Adolescents: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- PMID: 38856986
- PMCID: PMC11165417
- DOI: 10.1001/jamapediatrics.2024.1576
Global Prevalence of Overweight and Obesity in Children and Adolescents: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract
Importance: Overweight and obesity in childhood and adolescence is a global health issue associated with adverse outcomes throughout the life course.
Objective: To estimate worldwide prevalence of overweight and obesity in children and adolescents from 2000 to 2023 and to assess potential risk factors for and comorbidities of obesity.
Data sources: MEDLINE, Web of Science, Embase, and Cochrane.
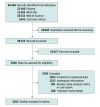
Study selection: The inclusion criteria were: (1) studies provided adequate information, (2) diagnosis based on body mass index cutoffs proposed by accepted references, (3) studies performed on general population between January 2000 and March 2023, (4) participants were younger than 18 years.
Data extraction and synthesis: The current study was performed in accordance with the Meta-analysis of Observational Studies in Epidemiology guidelines. DerSimonian-Laird random-effects model with Free-Tukey double arcsine transformation was used for data analysis. Sensitivity analysis, meta-regression, and subgroup analysis of obesity among children and adolescents were conducted.
Main outcomes and measures: Prevalence of overweight and obesity among children and adolescents assessed by World Health Organization, International Obesity Task Force, the US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or other national references.
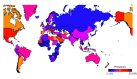
Results: A total of 2033 studies from 154 different countries or regions involving 45 890 555 individuals were included. The overall prevalence of obesity in children and adolescents was 8.5% (95% CI 8.2-8.8). We found that the prevalence varied across countries, ranging from 0.4% (Vanuatu) to 28.4% (Puerto Rico). Higher prevalence of obesity among children and adolescents was reported in countries with Human Development Index scores of 0.8 or greater and high-income countries or regions. Compared to 2000 to 2011, a 1.5-fold increase in the prevalence of obesity was observed in 2012 to 2023. Substantial differences in rates of obesity were noted when stratified by 11 risk factors. Children and adolescents with obesity had a high risk of depression and hypertension. The pooled estimates of overweight and excess weight in children and adolescents were 14.8% (95% CI 14.5-15.1) and 22.2% (95% CI 21.6-22.8), respectively.
Conclusions and relevance: This study's findings indicated 1 of 5 children or adolescents experienced excess weight and that rates of excess weight varied by regional income and Human Development Index. Excess weight among children and adolescents was associated with a mix of inherent, behavioral, environmental, and sociocultural influences that need the attention and committed intervention of primary care professionals, clinicians, health authorities, and the general public.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical