The impact of the Baby-Friendly Hospital Initiative on breastfeeding rates at maternity units in France
- PMID: 38857529
- PMCID: PMC11164413
- DOI: 10.1093/ije/dyae080
The impact of the Baby-Friendly Hospital Initiative on breastfeeding rates at maternity units in France
Abstract
Background: The Baby-Friendly Hospital Initiative (BFHI) is associated with improved breastfeeding outcomes in many high-income countries including the UK and the USA, but its effectiveness has never been evaluated in France. We investigated the impact of the BFHI on breastfeeding rates in French maternity units in 2010, 2016 and 2021 to assess if the BFHI aids to reduce inequalities in breastfeeding.
Methods: We examined breastfeeding in maternity units (exclusive, mixed and any breastfeeding) in mothers of singleton full-term newborns using the 2010 (n = 13 075), 2016 (n = 10 919) and 2021 (n = 10 209) French National Perinatal Surveys. We used mixed-effect hierarchical multinomial regression models adjusting for neonatal, maternal, maternity unit and French administrative department characteristics, and tested certain interactions.
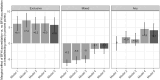
Results: The adjusted rate of exclusive breastfeeding was higher by +5.8 (3.4-8.1) points among mothers delivering in BFHI-accredited maternity units compared with those delivering in non-accredited units. When compared with average-weight newborns, this difference was sharper for infants with low birthweight: +14.9 (10.0-19.9) points when their birthweight was 2500 g. Mixed breastfeeding was lower by -1.7 points (-3.2-0) in BFHI-accredited hospitals, with no notable difference according to the neonatal or maternal characteristics.
Conclusion: Mothers delivering in BFHI-accredited maternity units had higher exclusive breastfeeding rates and lower mixed breastfeeding rates than those delivering in non-accredited maternity units. The positive impact of the BFHI was stronger among low-birthweight neonates, who are less often breastfed, helping reduce the gap for this vulnerable group while favouring mothers with higher education levels.
Keywords: Baby-Friendly Hospital Initiative; Breastfeeding; France; inequalities.
© The Author(s) 2024. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the International Epidemiological Association.
Conflict of interest statement
None declared.
Figures



References
-
- Victora CG, Bahl R, Barros AJ. et al. Breastfeeding in the 21st century: epidemiology, mechanisms, and lifelong effect. Lancet 2016;387:475–90. - PubMed
-
- World Health Organization, United Nations Children’s Fund, Wellstart International . The Baby-friendly Hospital Initiative: Monitoring and Reassessment: Tools to Sustain Progress. Geneva; 1991. https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/WHO-NHD-99.2 (12 April 2024, date last accessed).
-
- Howe-Heyman A, Lutenbacher M.. The Baby-Friendly Hospital Initiative as an intervention to improve breastfeeding rates: a review of the literature. JMWH 2016;61:77–102. - PubMed
-
- Beake S, Pellowe C, Dykes F, Schmied V, Bick D.. A systematic review of structured compared with non-structured breastfeeding programmes to support the initiation and duration of exclusive and any breastfeeding in acute and primary health care settings. Matern Child Nutr 2012;8:141–61. - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

