REDOMA: Bayesian random-effects dose-optimization meta-analysis using spike-and-slab priors
- PMID: 38857904
- PMCID: PMC11789924
- DOI: 10.1002/sim.10107
REDOMA: Bayesian random-effects dose-optimization meta-analysis using spike-and-slab priors
Abstract
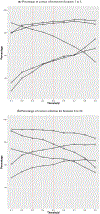
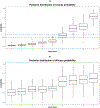
The rise of cutting-edge precision cancer treatments has led to a growing significance of the optimal biological dose (OBD) in modern oncology trials. These trials now prioritize the consideration of both toxicity and efficacy simultaneously when determining the most desirable dosage for treatment. Traditional approaches in early-phase oncology trials have conventionally relied on the assumption of a monotone relationship between treatment efficacy and dosage. However, this assumption may not hold valid for novel oncology therapies. In reality, the dose-efficacy curve of such treatments may reach a plateau at a specific dose, posing challenges for conventional methods in accurately identifying the OBD. Furthermore, achieving reliable identification of the OBD is typically not possible based on a single small-sample trial. With data from multiple phase I and phase I/II trials, we propose a novel Bayesian random-effects dose-optimization meta-analysis (REDOMA) approach to identify the OBD by synthesizing toxicity and efficacy data from each trial. The REDOMA method can address trials with heterogeneous characteristics. We adopt a curve-free approach based on a Gamma process prior to model the average dose-toxicity relationship. In addition, we utilize a Bayesian model selection framework that uses the spike-and-slab prior as an automatic variable selection technique to eliminate monotonic constraints on the dose-efficacy curve. The good performance of the REDOMA method is confirmed by extensive simulation studies.
Keywords: Bayesian methods; dose optimization; meta‐analysis; phase I/II trial; spike‐and‐slab prior.
© 2024 John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Drugs for preventing postoperative nausea and vomiting in adults after general anaesthesia: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Oct 19;10(10):CD012859. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD012859.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020. PMID: 33075160 Free PMC article.
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Apr 19;4(4):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 23;5:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub5. PMID: 33871055 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Dec 22;12(12):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Jan 9;1:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub3. PMID: 29271481 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
Assessing the comparative effects of interventions in COPD: a tutorial on network meta-analysis for clinicians.Respir Res. 2024 Dec 21;25(1):438. doi: 10.1186/s12931-024-03056-x. Respir Res. 2024. PMID: 39709425 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A rapid and systematic review of the clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of paclitaxel, docetaxel, gemcitabine and vinorelbine in non-small-cell lung cancer.Health Technol Assess. 2001;5(32):1-195. doi: 10.3310/hta5320. Health Technol Assess. 2001. PMID: 12065068
References
-
- Storer BE. Design and analysis of phase I clinical trials. Biometrics 1989: 925–937. - PubMed
-
- Gezmu M, Flournoy N. Group up-and-down designs for dose-finding. Journal of Statistical Planning and Inference 2006; 136. doi: 10.1016/j.jspi.2005.08.002 - DOI
-
- O’Quigley J, Pepe M, Fisher L. Continual reassessment method: a practical design for phase 1 clinical trials in cancer. Biometrics 1990: 33–48. - PubMed
-
- Babb J, Rogatko A, Zacks S. Cancer phase I clinical trials: efficient dose escalation with overdose control. Statistics in medicine 1998; 17(10): 1103–1120. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
