A highly neutralizing human monoclonal antibody targeting a novel linear epitope on staphylococcal enterotoxin B
- PMID: 38857905
- PMCID: PMC11182437
- DOI: 10.1080/21645515.2024.2360338
A highly neutralizing human monoclonal antibody targeting a novel linear epitope on staphylococcal enterotoxin B
Abstract
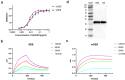
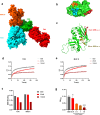
Staphylococcal Enterotoxin B (SEB), produced by Staphylococcus aureus (S. aureus), is a powerful superantigen that induces severe immune disruption and toxic shock syndrome (TSS) upon binding to MHC-II and TCR. Despite its significant impact on the pathogenesis of S. aureus, there are currently no specific therapeutic interventions available to counteract the mechanism of action exerted by this toxin. In this study, we have identified a human monoclonal antibody, named Hm0487, that specifically targets SEB by single-cell sequencing using PBMCs isolated from volunteers enrolled in a phase I clinical trial of the five-antigen S. aureus vaccine. X-ray crystallography studies revealed that Hm0487 exhibits high affinity for a linear B cell epitope in SEB (SEB138-147), which is located distantly from the site involved in the formation of the MHC-SEB-TCR ternary complex. Furthermore, in vitro studies demonstrated that Hm0487 significantly impacts the interaction of SEB with both receptors and the binding to immune cells, probably due to an allosteric effect on SEB rather than competing with receptors for binding sites. Moreover, both in vitro and in vivo studies validated that Hm0487 displayed efficient neutralizing efficacy in models of lethal shock and sepsis induced by either SEB or bacterial challenge. Our findings unveil an alternative mechanism for neutralizing the pathogenesis of SEB by Hm0487, and this antibody provides a novel strategy for mitigating both SEB-induced toxicity and S. aureus infection.
Keywords: Staphylococcus aureus; enterotoxin B; monoclonal antibody; neutralizing activity; structure.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Mechanisms mediating enhanced neutralization efficacy of staphylococcal enterotoxin B by combinations of monoclonal antibodies.J Biol Chem. 2015 Mar 13;290(11):6715-30. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M114.630715. Epub 2015 Jan 8. J Biol Chem. 2015. PMID: 25572397 Free PMC article.
-
mRNA-based platform for preventing and treating Staphylococcus aureus by targeted staphylococcal enterotoxin B.Front Immunol. 2024 Nov 21;15:1490044. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1490044. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39640268 Free PMC article.
-
Structural basis for the neutralization and specificity of Staphylococcal enterotoxin B against its MHC Class II binding site.MAbs. 2014 Jan-Feb;6(1):119-29. doi: 10.4161/mabs.27106. MAbs. 2014. PMID: 24423621 Free PMC article.
-
Staphylococcal toxic shock syndrome: superantigen-mediated enhancement of endotoxin shock and adaptive immune suppression.Immunol Res. 2014 Aug;59(1-3):182-7. doi: 10.1007/s12026-014-8538-8. Immunol Res. 2014. PMID: 24816557 Review.
-
Possible Role of Staphylococcal Enterotoxin B in the Pathogenesis of Autoimmune Diseases.Viral Immunol. 2015 Sep;28(7):354-9. doi: 10.1089/vim.2015.0017. Epub 2015 Jun 18. Viral Immunol. 2015. PMID: 26086678 Review.
Cited by
-
Disarming Staphylococcus aureus: Review of Strategies Combating This Resilient Pathogen by Targeting Its Virulence.Pathogens. 2025 Apr 15;14(4):386. doi: 10.3390/pathogens14040386. Pathogens. 2025. PMID: 40333163 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Sun C, Wang Q, Li W-T, Wen D-N, Chen C-H, Yang X, Shi W, Meng Q-H, Yao K-H, Qian S-Y. et al. Molecular characteristics and antimicrobial susceptibility of Staphylococcus aureus among children with respiratory tract infections in southwest China. World J Pediatr. 2020;16(3):284–92. doi:10.1007/s12519-019-00317-4. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
