Useful or not? The discussion of traditional Chinese medicine to treat COVID-19 on a Chinese social networking site
- PMID: 38857946
- PMCID: PMC11168149
- DOI: 10.1136/bmjgh-2023-014398
Useful or not? The discussion of traditional Chinese medicine to treat COVID-19 on a Chinese social networking site
Abstract
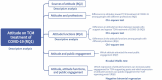
The use of traditional medicine is a global phenomenon, and the WHO advocated its appropriate integration into modern healthcare systems. However, there is a hot debate about the legitimacy of traditional medicine among the general public. Here, we investigated the debate in the Chinese digital context by analysing 1954 responses related to 100 questions about traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) treatment against COVID-19 on the Zhihu platform. Attitude function theory was applied to understand the reasons underlying public attitudes.Results showed that Zhihu users generally held a supportive attitude toward TCM. Their attitudes mainly came from their own experience and traditional media. The general users were more negative while medical professionals were more positive toward TCM. Ego defence (eg, derogating evidence sources) was used the most to support attitudes, followed by value expression (eg, believing in science). Supporters showed fewer expressions of faith (eg, the use of TCM is a kind of faith), politics (eg, supporting TCM is about politics) and science value (eg, TCM is a field of science), fewer ego defence, more patriotism and cultural confidence expressions (eg, TCM is a cultural pride) and more knowledge explanation (eg, TCM accelerates the metabolism of phlegm) than expected. Opposers showed fewer utilitarian and knowledge functions, fewer expressions of patriotism and more expressions of faith, politics and economics, but more ego defence functions than expected. Opposing posts were more likely to attract engagement than supporting and neutral posts. Posts that mentioned attitude functions generally attracted more engagement.Our findings indicate that TCM debate in modern China is not only relevant to medical science and health, but also rooted deeply in cultural ideology, politics and economics. The findings can provide global insights into the development of proactive policies and action plans that will help the integration of traditional medicine into modern healthcare systems.
Keywords: COVID-19; Public Health; Social Media.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2024. Re-use permitted under CC BY-NC. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None declared.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Knowledge of medical professionals, their practices, and their attitudes toward traditional Chinese medicine for the prevention and treatment of coronavirus disease 2019: A survey in Sichuan, China.PLoS One. 2021 Mar 16;16(3):e0234855. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0234855. eCollection 2021. PLoS One. 2021. PMID: 33725021 Free PMC article.
-
Weibo Users' Emotion and Sentiment Orientation in Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) During the COVID-19 Pandemic.Disaster Med Public Health Prep. 2022 Oct;16(5):1835-1838. doi: 10.1017/dmp.2021.259. Epub 2021 Aug 9. Disaster Med Public Health Prep. 2022. PMID: 34369351 Free PMC article.
-
[Rapid establishment of traditional Chinese medicine prevention and treatment of 2019-nCoV based on clinical experience and molecular docking].Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2020 Mar;45(6):1213-1218. doi: 10.19540/j.cnki.cjcmm.20200206.501. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2020. PMID: 32281327 Chinese.
-
Traditional Chinese Medicine as a complementary therapy in combat with COVID-19-A review of evidence-based research and clinical practice.J Adv Nurs. 2021 Apr;77(4):1635-1644. doi: 10.1111/jan.14673. Epub 2020 Nov 29. J Adv Nurs. 2021. PMID: 33174654
-
Application of Traditional Chinese Medicine and Systems Pharmacology in Drug Prevention and Treatment against COVID-19.Am J Chin Med. 2021;49(5):1045-1061. doi: 10.1142/S0192415X21500506. Am J Chin Med. 2021. PMID: 34225580 Review.
References
-
- World Health Organization . WHO convenes first high-level global summit on traditional medicine to explore evidence base, opportunities to accelerate health for all. Available: https://www.who.int/news/item/10-08-2023-who-convenes-first-high-level-g... [Accessed 27 Aug 2023].
-
- Pi G. Collision and Confluence: the path of change in modern Chinese medicine. Beijing Cultural Review 2017;1:42–51.
-
- Jian C, Qilong C, Shibing S. Thoughts and exploration of traditional Chinese precision medical treatment. Modernization of Traditional Chinese Medicine and Materia Medica-World Science and Technology 2016;18:557–62.
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical