Assessing children who are acutely ill in general practice using the National PEWS and LqSOFA clinical scores: a retrospective cohort study
- PMID: 38858101
- PMCID: PMC11497154
- DOI: 10.3399/BJGP.2023.0638
Assessing children who are acutely ill in general practice using the National PEWS and LqSOFA clinical scores: a retrospective cohort study
Abstract
Background: Clinical tools are needed in general practice to help identify children who are seriously ill. The Liverpool quick Sequential Organ Failure Assessment (LqSOFA) was validated in an emergency department and performed well. The National Paediatric Early Warning System (PEWS) has been introduced in hospitals throughout England with hopes for implementation in general practice.
Aim: To validate the LqSOFA and National PEWS in general practice.
Design and setting: Secondary analysis of 6703 children aged <5 years presenting to 225 general practices in England and Wales with acute illnesses, linked to hospital data.
Method: Variables from the LqSOFA and National PEWS were mapped onto study data to calculate score totals. A primary outcome of admission within 2 days of GP consultation was used to calculate sensitivity, specificity, negative predictive values (NPVs), positive predictive values (PPVs), and area under the receiver operating characteristic curve (AUC).
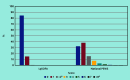
Results: A total of 104/6703 children were admitted to hospital within 2 days (pre-test probability 1.6%) of GP consultation. The sensitivity of the LqSOFA was 30.6% (95% confidence interval [CI] = 21.8% to 41.0%), with a specificity of 84.7% (95% CI = 83.7% to 85.6%), PPV of 3.0% (95% CI = 2.1% to 4.4%), NPV of 98.7% (95% CI = 98.4% to 99.0%), and AUC of 0.58 (95% CI = 0.53 to 0.63). The sensitivity of the National PEWS was 81.0% (95% CI = 71.0% to 88.1%), with a specificity of 32.5% (95% CI = 31.2% to 33.8%), PPV of 1.9% (95% CI = 1.5% to 2.5%), NPV of 99.1% (95% CI = 98.4% to 99.4%), and AUC of 0.66 (95% CI = 0.59 to 0.72).
Conclusion: Although the NPVs appear useful, owing to low pre-test probabilities rather than discriminative ability, neither tool accurately identified admissions to hospital. Unconsidered use by GPs could result in unsustainable referrals.
Keywords: child health; clinical prediction rule; early warning score; general practice; retrospective studies; triage.
© The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Gill PJ, Goldacre MJ, Mant D, et al. Increase in emergency admissions to hospital for children aged under 15 in England, 1999–2010: national database analysis. Arch Dis Child. 2013;98(5):328–334. - PubMed
-
- Neill S, Roland D, Thompson M, et al. Why are acute admissions to hospital of children under 5 years of age increasing in the UK? Arch Dis Child. 2018;103(10):917–919. - PubMed
-
- Okike IO, Ribeiro S, Ramsay ME, et al. Trends in bacterial, mycobacterial, and fungal meningitis in England and Wales 2004–11: an observational study. Lancet Infec Dis. 2014;14(4):301–307. - PubMed
-
- Public Health England Invasive meningococcal disease in England: annual laboratory confirmed reports for epidemiological year 2018 to 2019. 2019 https://assets.publishing.service.gov.uk/media/5db6b581ed915d1d07006e78/... (accessed 26 Sep 2024).
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
