Highly Soluble Dacarbazine Multicomponent Crystals Less Prone to Photodegradation
- PMID: 38858241
- PMCID: PMC11220790
- DOI: 10.1021/acs.molpharmaceut.4c00393
Highly Soluble Dacarbazine Multicomponent Crystals Less Prone to Photodegradation
Abstract
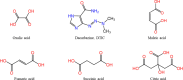
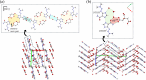
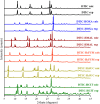
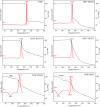
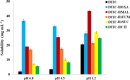
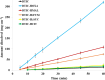
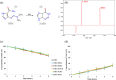
Dacarbazine (DTIC) is a widely prescribed oncolytic agent to treat advanced malignant melanomas. Nevertheless, the drug is known for exhibiting low and pH-dependent solubility, in addition to being photosensitive. These features imply the formation of the inactive photodegradation product 2-azahypoxanthine (2-AZA) during pharmaceutical manufacturing and even drug administration. We have focused on developing novel DTIC salt/cocrystal forms with enhanced solubility and dissolution behaviors to overcome or minimize this undesirable biopharmaceutical profile. By cocrystallization techniques, two salts, two cocrystals, and one salt-cocrystal have been successfully prepared through reactions with aliphatic carboxylic acids. A detailed structural study of these new multicomponent crystals was conducted using X-ray diffraction (SCXRD, PXRD), spectroscopic (FT-IR and 1H NMR), and thermal (TG and DSC) analyses. Most DTIC crystal forms reported display substantial enhancements in solubility (up to 19-fold), with faster intrinsic dissolution rates (from 1.3 to 22-fold), contributing positively to reducing the photodegradation of DTIC in solution. These findings reinforce the potential of these new solid forms to enhance the limited DTIC biopharmaceutical profile.
Keywords: cocrystal; cocrystallization; dacarbazine; salt; solubility; stability.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures
References
-
- Liu L.; Wang J. R.; Mei X. Enhancing the Stability of Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients by the Cocrystal Strategy. CrystEngComm 2022, 24 (11), 2002–2022. 10.1039/D1CE01327K. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

