Hybrid Chin Advancement: Combining Fat and Sliced Cartilage Grafts for Chin Augmentation During Rhinoplasty
- PMID: 38858246
- PMCID: PMC11281964
- DOI: 10.1007/s00266-024-04137-4
Hybrid Chin Advancement: Combining Fat and Sliced Cartilage Grafts for Chin Augmentation During Rhinoplasty
Abstract
Background: Facial balance significantly impacts aesthetics, particularly in the middle and lower thirds. Patients with chin retrusion often benefit from sagittal plane chin advancement in rhinoplasty, enhancing surgical outcomes and satisfaction.
Objectives: This article presents a method for analyzing chin deformities and discusses a hybrid treatment approach to harmonize facial features, complementing rhinoplasty.
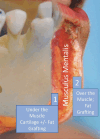
Methods: The chin positions of patients treated by the senior author were assessed. A retrospective analysis included 49 patients with chin retrusion of 2.5-6 mm. Among them, 22 patients initially offered chin implants declined, leading to planned chin augmentation. Fat grafting was exclusively performed for 20 patients lacking sufficient cartilage. The "Hybrid Chin Advancement" technique involved supporting tissues beneath muscles with nasal septum cartilage and fat injections and tissues above muscles with fat injection alone.
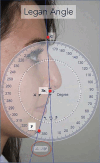
Results: Pre- and postoperative Legan angle measurements and chin advancements were compared across three groups. While preoperative Legan angles were statistically similar, postoperative Legan angles and advancement changes were significantly higher in the implant group (p < 0.0001). Comparing hybrid chin advancement and fat grafting groups, postoperative Legan angles and advancement changes were significantly higher in the hybrid chin group (p < 0.0001).
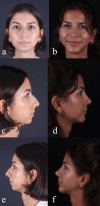
Conclusions: Fat grafting suffices for mild advancements (~ 2 mm), while the hybrid chin method is effective for moderate advancements (~ 4 mm). For advancements exceeding 6 mm, implants or osseous genioplasty are optimal. Our study's hybrid approach offers an easy, safe, and reliable method for achieving facial harmony in the lower two-thirds without compromising patient expectations.
Level of evidence iv: This journal requires that authors assign a level of evidence to each article. For a full description of these Evidence-Based Medicine ratings, please refer to the Table of Contents or the online Instructions to Authors www.springer.com/00266 .
Keywords: Cartilage graft; Chin augmentation; Fat grafting; Rhinoplasty.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest to disclose.
Figures


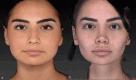





Similar articles
-
Chin Dysmorphology in the Primary Rhinoplasty Population: Prevalence, Objective Analysis, and Implications.Aesthetic Plast Surg. 2024 Jan;48(2):177-186. doi: 10.1007/s00266-023-03438-4. Epub 2023 Jul 10. Aesthetic Plast Surg. 2024. PMID: 37430011 Review.
-
Chin Microgenia: A Clinical Comparative Study.Aesthetic Plast Surg. 2015 Oct;39(5):651-8. doi: 10.1007/s00266-015-0518-4. Epub 2015 Jul 1. Aesthetic Plast Surg. 2015. PMID: 26130400
-
Free Crushed Cartilage Filler Graft to Optimize Tip Aesthetics in Asian Rhinoplasty.Aesthetic Plast Surg. 2025 May;49(10):2735-2745. doi: 10.1007/s00266-024-04369-4. Epub 2024 Sep 25. Aesthetic Plast Surg. 2025. PMID: 39322839
-
Autogenous Fat Grafting for Chin Augmentation: A Preliminarily Clinical Study of Cosmetic Outcome.J Craniofac Surg. 2015 Oct;26(7):e625-7. doi: 10.1097/SCS.0000000000002140. J Craniofac Surg. 2015. PMID: 26468847
-
Custom-Made Implant Fabrication for Chin Augmentation Using Piled-Up Expanded Polytetrafluoroethylene Sheets: An Innovative Surgical Technique and Literature Review.Aesthetic Plast Surg. 2024 Jun;48(11):2018-2024. doi: 10.1007/s00266-024-03918-1. Epub 2024 Mar 18. Aesthetic Plast Surg. 2024. PMID: 38499874 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Paul MA, Kamali P, Chen AD, Ibrahim AMS, Wu W, Becherer BE, Medin C, Lin SJ (2018) Assessment of functional rhinoplasty with spreader grafting using acoustic rhinomanometry and validated outcome measurements. Plast Reconstr Surg Glob Open 6(3):e1615. 10.1097/GOX.0000000000001615 10.1097/GOX.0000000000001615 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Kuçuker I, Aksakal IA, Yosma E et al (2016) Assessing the expectations of patients demanding rhinoplasty on profile photographs using proportional measurements and simulation programs. Turk J Plast Surg. 10.5152/TurkJPlastSurg.2016.194010.5152/TurkJPlastSurg.2016.1940 - DOI
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

