The miR-30-5p/TIA-1 axis directs cellular senescence by regulating mitochondrial dynamics
- PMID: 38858355
- PMCID: PMC11164864
- DOI: 10.1038/s41419-024-06797-1
The miR-30-5p/TIA-1 axis directs cellular senescence by regulating mitochondrial dynamics
Abstract
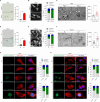
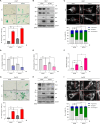
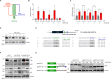
Senescent cells exhibit a diverse spectrum of changes in their morphology, proliferative capacity, senescence-associated secretory phenotype (SASP) production, and mitochondrial homeostasis. These cells often manifest with elongated mitochondria, a hallmark of cellular senescence. However, the precise regulatory mechanisms orchestrating this phenomenon remain predominantly unexplored. In this study, we provide compelling evidence for decreases in TIA-1, a pivotal regulator of mitochondrial dynamics, in models of both replicative senescence and ionizing radiation (IR)-induced senescence. The downregulation of TIA-1 was determined to trigger mitochondrial elongation and enhance the expression of senescence-associated β-galactosidase, a marker of cellular senescence, in human foreskin fibroblast HS27 cells and human keratinocyte HaCaT cells. Conversely, the overexpression of TIA-1 mitigated IR-induced cellular senescence. Notably, we identified the miR-30-5p family as a novel factor regulating TIA-1 expression. Augmented expression of the miR-30-5p family was responsible for driving mitochondrial elongation and promoting cellular senescence in response to IR. Taken together, our findings underscore the significance of the miR-30-5p/TIA-1 axis in governing mitochondrial dynamics and cellular senescence.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Inhibition of transglutaminase 2 inhibits ionizing radiation-induced cellular senescence in skin keratinocytes in vitro.IUBMB Life. 2024 Dec;76(12):1252-1263. doi: 10.1002/iub.2906. Epub 2024 Aug 14. IUBMB Life. 2024. PMID: 39139071
-
MiR-718-mediated inhibition of prohibitin 1 influences mitochondrial dynamics, proliferation, and migration of keratinocytes.Mitochondrion. 2025 Sep;84:102041. doi: 10.1016/j.mito.2025.102041. Epub 2025 Apr 17. Mitochondrion. 2025. PMID: 40252889
-
Unveiling Selenoprotein T as a novel regulator of cardiomyocyte senescence: pivotal role of the CD36 receptor in AC16 human cardiomyocytes.Geroscience. 2025 Jul 1. doi: 10.1007/s11357-025-01759-7. Online ahead of print. Geroscience. 2025. PMID: 40593378
-
Mitochondrial dysfunction in the regulation of aging and aging-related diseases.Cell Commun Signal. 2025 Jun 19;23(1):290. doi: 10.1186/s12964-025-02308-7. Cell Commun Signal. 2025. PMID: 40537801 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Advancements in Targeting Macrophage Senescence for Age-Associated Conditions.Aging Dis. 2024 Sep 14;16(4):2201-2236. doi: 10.14336/AD.2024.0720. Aging Dis. 2024. PMID: 39500353 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Extracellular vesicle-encapsulated microRNA signatures of cigarette smoking and smoking-related harm.Respir Med. 2025 Sep;246:108226. doi: 10.1016/j.rmed.2025.108226. Epub 2025 Jun 28. Respir Med. 2025. PMID: 40588139
-
Anti-senescence therapies: a new concept to address cardiovascular disease.Cardiovasc Res. 2025 May 23;121(5):730-747. doi: 10.1093/cvr/cvaf030. Cardiovasc Res. 2025. PMID: 40036821 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Senescence, NK cells, and cancer: navigating the crossroads of aging and disease.Front Immunol. 2025 Apr 4;16:1565278. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1565278. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40255394 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Underestimated Role of Iron in Frontotemporal Dementia: A Narrative Review.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Dec 3;25(23):12987. doi: 10.3390/ijms252312987. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39684697 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

