Genotype × environment interactions in gene regulation and complex traits
- PMID: 38858456
- PMCID: PMC11492161
- DOI: 10.1038/s41588-024-01776-w
Genotype × environment interactions in gene regulation and complex traits
Abstract
Genotype × environment interactions (GxE) have long been recognized as a key mechanism underlying human phenotypic variation. Technological developments over the past 15 years have dramatically expanded our appreciation of the role of GxE in both gene regulation and complex traits. The richness and complexity of these datasets also required parallel efforts to develop robust and sensitive statistical and computational approaches. Although our understanding of the genetic architecture of molecular and complex traits has been maturing, a large proportion of complex trait heritability remains unexplained. Furthermore, there are increasing efforts to characterize the effect of environmental exposure on human health. We therefore review GxE in human gene regulation and complex traits, advocating for a comprehensive approach that jointly considers genetic and environmental factors in human health and disease.
© 2024. Springer Nature America, Inc.
Figures

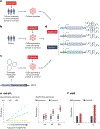
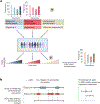
Similar articles
-
Genotype by environment interactions for reproductive performance of North American purebred sows between North America and Southeast Asia.J Anim Sci. 2025 Jan 4;103:skaf191. doi: 10.1093/jas/skaf191. J Anim Sci. 2025. PMID: 40577530 Free PMC article.
-
Bias and Precision of Parameter Estimates from Models Using Polygenic Scores to Estimate Environmental and Genetic Parental Influences.Behav Genet. 2021 May;51(3):279-288. doi: 10.1007/s10519-020-10033-9. Epub 2020 Dec 10. Behav Genet. 2021. PMID: 33301082 Free PMC article.
-
Genotype × Environment Interaction in Smoking Behaviors: A Systematic Review.Nicotine Tob Res. 2017 Apr 1;19(4):387-400. doi: 10.1093/ntr/ntw153. Nicotine Tob Res. 2017. PMID: 27613915 Free PMC article.
-
Interactions between genetic variation and cellular environment in skeletal muscle gene expression.PLoS One. 2018 Apr 16;13(4):e0195788. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0195788. eCollection 2018. PLoS One. 2018. PMID: 29659628 Free PMC article.
-
Research review: gene-environment interaction research in youth depression - a systematic review with recommendations for future research.J Child Psychol Psychiatry. 2011 Dec;52(12):1223-38. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-7610.2011.02466.x. Epub 2011 Sep 29. J Child Psychol Psychiatry. 2011. PMID: 21954964 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Machine learning reveals complex genetics of fungal resistance in sorghum grain mold.Heredity (Edinb). 2025 Aug;134(8):485-499. doi: 10.1038/s41437-025-00783-9. Epub 2025 Jul 19. Heredity (Edinb). 2025. PMID: 40684039
-
Higher eQTL power reveals signals that boost GWAS colocalization.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2025 Aug 5:2025.08.05.668745. doi: 10.1101/2025.08.05.668745. bioRxiv. 2025. PMID: 40799583 Free PMC article. Preprint.
-
Genetics and Environment Distinctively Shape the Human Immune Cell Epigenome.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2025 Jan 4:2023.06.29.546792. doi: 10.1101/2023.06.29.546792. bioRxiv. 2025. PMID: 37425926 Free PMC article. Preprint.
-
Epistasis and cryptic QTL identified using modified bulk segregant analysis of copper resistance in budding yeast.Genetics. 2025 Apr 17;229(4):iyaf026. doi: 10.1093/genetics/iyaf026. Genetics. 2025. PMID: 39989051
-
Genotype-by-environment interactions shape ubiquitin-proteasome system activity.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Nov 21:2024.11.21.624644. doi: 10.1101/2024.11.21.624644. bioRxiv. 2024. PMID: 39605480 Free PMC article. Preprint.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- R01GM109215/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Institute of General Medical Sciences (NIGMS)
- R01 ES033634/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- F30GM151855/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Institute of General Medical Sciences (NIGMS)
- R01 GM109215/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL162574/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01ES033634/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Institute of Environmental Health Sciences (NIEHS)
- R35 GM138121/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- F30 GM151855/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01HL162574/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (NHLBI)
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

