Minimally invasive versus open ileal ureter with ileocystoplasty: comparative outcomes and 5-year experience
- PMID: 38858691
- PMCID: PMC11163719
- DOI: 10.1186/s12894-024-01509-5
Minimally invasive versus open ileal ureter with ileocystoplasty: comparative outcomes and 5-year experience
Abstract
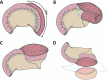
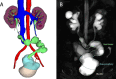
Purpose: To present the experience of ileal ureter with ileocystoplasty (IUC), and compare the outcomes of IUC in minimally invasive procedures to open procedures.
Patients and methods: From December 2017 to April 2023, twenty patients underwent IUC in open or minimally invasive (including laparoscopic and robotic) procedures. The baseline characteristics, perioperative data and follow-up outcomes were collected. Success was defined as relief of clinical symptoms, stable postoperative serum creatine and absence of radiographic obstruction. The perioperative and follow-up outcomes of open procedures and minimally invasive procedures were compared.
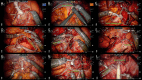
Results: The etiology included pelvic irradiation (14/20), urinary tuberculosis (3/20) and surgical injury (3/20). Bilateral ureter strictures were repaired in 15 cases. The surgeries conducted consisted of open procedures in 9 patients and minimally invasive procedures in 11 patients. Compared to open procedures, minimally invasive surgeries had less median estimated blood loss (EBL) (100 ml vs. 300 min, p = 0.010) and shorter postoperative hospitalization (27 d vs. 13 d, p = 0.004). Two patients in the open group experienced grade 3 complications (sigmoid fistula and acute cholecystitis in one patient, and pulmonary embolism in another patient). Over a median follow-up period of 20.1 months, the median bladder functional capacity was 300 ml, with a 100% success rate of IUC.
Conclusion: IUC is feasible in both open and minimally invasive procedures, with acceptable complications and a high success rate. Minimally invasive procedures can have less EBL and shorter postoperative hospitalization than open procedure. However, prospective studies with larger groups and longer follow-up are needed.
Keywords: Ileal ureter replacement; Ileocystoplasty; Minimally invasive surgery; Ureteral stricture with bladder contracture.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Open, laparoscopic, and robotic ureteroneocystotomy for benign and malignant ureteral lesions: a comparison of over 100 minimally invasive cases.J Endourol. 2014 Dec;28(12):1455-9. doi: 10.1089/end.2014.0243. J Endourol. 2014. PMID: 25390972
-
Totally Intracorporeal Robot-assisted Unilateral or Bilateral Ileal Ureter Replacement for the Treatment of Ureteral Strictures: Technique and Outcomes from a Single Center.Eur Urol. 2023 Dec;84(6):561-570. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2023.04.022. Epub 2023 May 22. Eur Urol. 2023. PMID: 37225525
-
Ileal ureter replacement and ileocystoplasty for the treatment of bilateral ureteral strictures and bladder contracture: technique and outcomes.Minerva Urol Nephrol. 2024 Feb;76(1):97-109. doi: 10.23736/S2724-6051.23.05492-7. Minerva Urol Nephrol. 2024. PMID: 38426424
-
Minimally Invasive Techniques for Bladder Reconstruction.Curr Urol Rep. 2018 Apr 13;19(6):39. doi: 10.1007/s11934-018-0787-y. Curr Urol Rep. 2018. PMID: 29654429 Review.
-
Robotic-assisted laparoscopic reconstructive surgery in the lower urinary tract.Curr Urol Rep. 2013 Aug;14(4):333-41. doi: 10.1007/s11934-013-0328-7. Curr Urol Rep. 2013. PMID: 23740381 Review.
References
-
- Li Z, Wang X, Ying Y, Li X, Zhu W, Meng C, Han G, Liu J, Wang J, Huang Y et al. Health-related quality of life (HRQoL), anxiety and depression in patients with ureteral stricture: a multi-institutional study. World J Urol 2022. - PubMed
-
- Cheng S, Fan S, Wang J, Xiong S, Li X, Xu Y, Li Z, Guan H, Zhang P, Zhu H, et al. Laparoscopic and robotic ureteroplasty using onlay flap or graft for the management of long proximal or middle ureteral strictures: our experience and strategy. Int Urol Nephrol. 2021;53(3):479–88. doi: 10.1007/s11255-020-02679-5. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

