Mechanical properties of combined packable and high-filled flowable composite used for the fixed retainer: an in vitro study
- PMID: 38858745
- PMCID: PMC11165839
- DOI: 10.1186/s12903-024-04437-w
Mechanical properties of combined packable and high-filled flowable composite used for the fixed retainer: an in vitro study
Abstract
Background: Clinicians often utilize both flowable and packable composites concurrently in bonding fixed retainers. Thus, this study aimed to assess the synergistic effect of these composites in the bonding process.
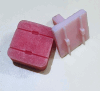
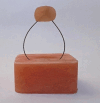
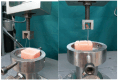
Methods: This in vitro study divided specimens into three groups: flowable composite (nano-hybrid, Tetric N-Flow, Ivoclar Vivadent), packable composite (nano-hybrid, Tetric N-ceram, Ivoclar Vivadent), and combined use of flowable and packable composite. Shear bond strength (SBS), adhesive remnant index (ARI), and wire pull-out resistance were compared among the groups. Statistical analyses were conducted using ANOVA and Tukey tests to compare study groups. Additionally, Chi-square and Kruskal-Wallis tests were employed to analyze the ARI index among the groups.
Results: ANOVA results indicated no statistically significant differences among test groups (P = 0.129) regarding SBS. However, a significant difference existed between flowable and packable composite groups (P = 0.01) regarding ARI scores. Among the study groups, flowable composite exhibited the highest frequencies of ARI scores of 1 and 2, whereas packable composite showed the highest frequency of ARI scores of 0. The combined group had higher frequencies of ARI scores of 0 and 1 compared to the flowable composite. The wire pull-out test revealed that the combined application of flowable and packable composite resulted in significantly lower detachments compared to the packable composite alone (P = 0.008). However, no significant differences were observed in the comparisons between the flowable-packable (P = 0.522) and combined-flowable (P = 0.128) groups.
Conclusion: The combined use of flowable and packable composites for fixed retainers demonstrated adequate shear bond strength and ideal ARI scores, suggesting it as a suitable adhesive system for bonding orthodontic fixed retainers.
Keywords: Adhesive; Biomedical and dental material; Composite; Fixed retainer.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




References
-
- Egli F, Bovali E, Kiliaridis S, Cornelis MA. Indirect vs direct bonding of mandibular fixed retainers in orthodontic patients: comparison of retainer failures and posttreatment stability. A 2-year follow-up of a single-center randomized controlled trial. Am J Orthod Dentofac Orthop. 2017;151(1):15–27. doi: 10.1016/j.ajodo.2016.09.009. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

