Exploration of tissue fixation methods suitable for digital pathological studies of the testis
- PMID: 38858777
- PMCID: PMC11163764
- DOI: 10.1186/s40001-024-01921-5
Exploration of tissue fixation methods suitable for digital pathological studies of the testis
Abstract
Background: The way of testicular tissue fixation directly affects the correlation and structural integrity between connective tissue and seminiferous tubules, which is essential for the study of male reproductive development. This study aimed to find the optimal fixative and fixation time to produce high-quality testicular histopathological sections, and provided a suitable foundation for in-depth study of male reproductive development with digital pathology technology.
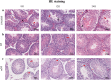
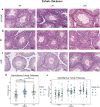
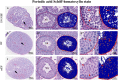
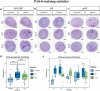
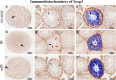
Methods: Testes were removed from both sides of 25 male C57BL/6 mice. Samples were fixed in three different fixatives, 10% neutral buffered formalin (10% NBF), modified Davidson's fluid (mDF), and Bouin's Fluid (BF), for 8, 12, and 24 h, respectively. Hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) staining, periodic acid Schiff-hematoxylin (PAS-h) staining, and immunohistochemistry (IHC) were used to evaluate the testicle morphology, staging of mouse seminiferous tubules, and protein preservation. Aperio ScanScope CS2 panoramic scanning was used to perform quantitative analyses.
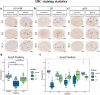
Results: H&E staining showed 10% NBF resulted in an approximately 15-17% reduction in the thickness of seminiferous epithelium. BF and mDF provided excellent results when staining acrosomes with PAS-h. IHC staining of synaptonemal complexes 3 (Sycp3) was superior in mDF compared to BF-fixed samples. Fixation in mDF and BF improved testis tissue morphology compared to 10% NBF.
Conclusions: Quantitative analysis showed that BF exhibited a very low IHC staining efficiency and revealed that mouse testes fixed for 12 h with mDF, exhibited morphological details, excellent efficiency of PAS-h staining for seminiferous tubule staging, and IHC results. In addition, the morphological damage of testis was prolonged with the duration of fixation time.
Keywords: Digital pathology; Fixative; HE staining; IHC staining; Mouse testis; PAS staining.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
All authors have been notified of the article and declared no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Fixation of testes and eyes using a modified Davidson's fluid: comparison with Bouin's fluid and conventional Davidson's fluid.Toxicol Pathol. 2002 Jul-Aug;30(4):524-33. doi: 10.1080/01926230290105721. Toxicol Pathol. 2002. PMID: 12187944
-
Morphology of rat testis preserved in three different fixatives.J Huazhong Univ Sci Technolog Med Sci. 2011 Apr;31(2):178-180. doi: 10.1007/s11596-011-0247-0. Epub 2011 Apr 20. J Huazhong Univ Sci Technolog Med Sci. 2011. PMID: 21505980
-
Different fixatives influence morphology, antigen preservation, and TUNEL staining in chicken (Gallus gallus) testis.Acta Histochem. 2021 Dec;123(8):151822. doi: 10.1016/j.acthis.2021.151822. Epub 2021 Nov 30. Acta Histochem. 2021. PMID: 34861475
-
Staging of mouse seminiferous tubule cross-sections.Methods Mol Biol. 2009;558:263-77. doi: 10.1007/978-1-60761-103-5_16. Methods Mol Biol. 2009. PMID: 19685330 Review.
-
Special symposium: fixation and tissue processing models.Biotech Histochem. 2009 Oct;84(5):185-93. doi: 10.3109/10520290903039052. Biotech Histochem. 2009. PMID: 19886755 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Polystyrene Microplastics-Induced Thyroid Dysfunction in Mice: A Study of Gene Expression, Oxidative Stress, and Histopathological Changes.Vet Med Sci. 2025 May;11(3):e70393. doi: 10.1002/vms3.70393. Vet Med Sci. 2025. PMID: 40367361 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

