Genetically predicted associations between circulating cytokines and autoimmune diseases: a bidirectional two-sample Mendelian randomization
- PMID: 38860028
- PMCID: PMC11163916
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1404260
Genetically predicted associations between circulating cytokines and autoimmune diseases: a bidirectional two-sample Mendelian randomization
Abstract
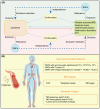
Objectives: Previous studies have indicated a correlation between cytokines and autoimmune diseases. yet the causality remains uncertain. Through Mendelian Randomization (MR) analysis, we aimed to investigate the causal relationships between genetically predicted levels of 91 cytokines and three autoimmune diseases: Multiple Sclerosis (MS), Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE), and Hashimoto's Thyroiditis (HT).
Methods: A bidirectional two-sample MR approach was utilized to assess the causal relationships between cytokines and MS, SLE, and HT. The datasets included 47,429 MS cases and 68,374 controls, 5,201 SLE cases and 9,066 controls, and 16,191 HT cases with 210,612 controls. Data on 91 cytokines comprised 14,824 participants. Causal analyses primarily employed inverse variance weighted, weighted median, and MR-Egger methods, with sensitivity analyses including heterogeneity and pleiotropy assessment.
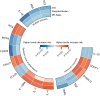
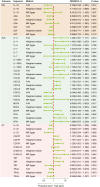
Results: Genetically predicted levels of IL-18 (OR = 0.706; 95% C.I. 0.538-0.925), ADA (OR = 0.808; 95% C.I. 0.673-0.970), and SCF (OR = 0.898; 95% C.I. 0.816-0.987) were associated with a decreased risk of MS. IL-4 (OR = 1.384; 95% C.I. 1.081-1.771), IL-7 (OR = 1.401; 95% C.I. 1.010-1.943), IL-10RA (OR = 1.266; 95% C.I. 1.004-1.596), CXCL5 (OR = 1.170; 95% C.I. 1.021-1.341), NTN (OR = 1.225; 95% C.I. 1.004-1.496), FGF23 (OR = 0.644; 95% C.I. 0.460-0.902), and MCP4 (OR = 0.665; 95% C.I. 0.476-0.929) were associated with SLE risk. CDCP1 (OR = 1.127; 95% C.I. 1.008-1.261), IL-33 (OR = 0.852; 95% C.I. 0.727-0.999), and TRAIL (OR = 0.884; 95% C.I. 0.799-0.979) were associated with HT risk. Bidirectional MR results suggest the involvement of CCL19, IL-13, SLAM, ARTN, Eotaxin, IL-22RA1, ADA, and MMP10 in the downstream development of these diseases.
Conclusions: Our findings support causal relationships between certain cytokines and the risks of MS, SLE, and HT, identifying potential biomarkers for diagnosis and prevention. Additionally, several cytokines previously unexplored in these autoimmune disease contexts were discovered, laying new groundwork for the study of disease mechanisms and therapeutic potentials.
Keywords: cytokine; hashimoto’s thyroiditis; mendelian randomization; multiple sclerosis; systemic lupus erythematosus.
Copyright © 2024 Jie, Gong, Luo, Yang and Guo.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Causality of Hashimoto's Thyroiditis to Thyroid Cancer: A 2-S Mendelian Randomization Study.Endocr Pract. 2024 Dec;30(12):1158-1165. doi: 10.1016/j.eprac.2024.09.009. Epub 2024 Sep 18. Endocr Pract. 2024. PMID: 39304132
-
The causal associations of inflammatory cytokines with obesity and systemic lupus erythematosus: A Mendelian randomization study.Int J Rheum Dis. 2024 Jun;27(6):e15214. doi: 10.1111/1756-185X.15214. Int J Rheum Dis. 2024. PMID: 38831532
-
[Causal relationship between autoimmune diseases and aplastic anemia: A Mendelian randomization study].Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 2025 Apr 20;45(4):871-879. doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2025.04.23. Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 2025. PMID: 40294938 Free PMC article. Chinese.
-
Association between Omega-3 fatty acids and autoimmune disease: Evidence from the umbrella review and Mendelian randomization analysis.Autoimmun Rev. 2024 Nov;23(11):103651. doi: 10.1016/j.autrev.2024.103651. Epub 2024 Sep 30. Autoimmun Rev. 2024. PMID: 39357585 Review.
-
The roles of pyroptosis in the pathogenesis of autoimmune diseases.Life Sci. 2024 Dec 15;359:123232. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2024.123232. Epub 2024 Nov 12. Life Sci. 2024. PMID: 39537097 Review.
Cited by
-
IL-7 in autoimmune diseases: mechanisms and therapeutic potential.Front Immunol. 2025 Apr 17;16:1545760. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1545760. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40313966 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

