Knockdown of Glycolysis-Related LINC01070 Inhibits the Progression of Breast Cancer
- PMID: 38860098
- PMCID: PMC11163994
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.60093
Knockdown of Glycolysis-Related LINC01070 Inhibits the Progression of Breast Cancer
Abstract
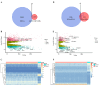
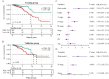
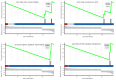
Accumulative evidence confirms that glycolysis and long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) are closely associated with tumor development. The aim of this study was to construct a novel prognostic model based on glycolysis-related lncRNAs (GRLs) in breast cancer patients. By performing Pearson correlation analysis and Lasso regression analysis on differentially expressed genes and lncRNAs associated with glycolysis in the Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) and Gene Set Enrichment Analysis (GSEA) datasets, we identified nine GRLs and constructed associated prognostic risk signature. Kaplan-Meier survival analysis and univariate and multivariate Cox analysis showed that patients in the low-risk group had a better prognosis. The receiver operator characteristics (ROC) curves showed that the area under the curve (AUC) of the prognostic risk signature predicting patients' overall survival at 1-, 3- and 5- years was 0.78, 0.71, and 0.71, respectively. Moreover, the validation curves also showed that the signature had better diagnostic efficacy and clinical predictive power. Furthermore, clone formation assay, EdU assay, and Transwell assay showed that knockdown of LINC01070 inhibited breast cancer progression. We developed a prognostic risk-associated GRLs signature that can accurately predict the breast cancer patient's prognostic status, and LINC01070 can be used as a potential biomarker for the prognosis of breast cancer patients.
Keywords: breast cancer; glycolysis; linc01070; lncrnas; nomogram; risk model.
Copyright © 2024, Hu et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Identification of a Novel Glycolysis-Related LncRNA Signature for Predicting Overall Survival in Patients With Bladder Cancer.Front Genet. 2021 Aug 19;12:720421. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2021.720421. eCollection 2021. Front Genet. 2021. PMID: 34490046 Free PMC article.
-
Construction of prognostic signature of breast cancer based on N7-Methylguanosine-Related LncRNAs and prediction of immune response.Front Genet. 2022 Oct 24;13:991162. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2022.991162. eCollection 2022. Front Genet. 2022. PMID: 36353118 Free PMC article.
-
Construction and validation of a glycolysis-related lncRNA signature for prognosis prediction in Stomach Adenocarcinoma.Front Genet. 2022 Oct 14;13:794621. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2022.794621. eCollection 2022. Front Genet. 2022. PMID: 36313430 Free PMC article.
-
A Signature of Autophagy-Related Long Non-coding RNA to Predict the Prognosis of Breast Cancer.Front Genet. 2021 Mar 16;12:569318. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2021.569318. eCollection 2021. Front Genet. 2021. PMID: 33796128 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of an m6A-Related lncRNA Signature for Predicting the Prognosis in Patients With Kidney Renal Clear Cell Carcinoma.Front Oncol. 2021 May 26;11:663263. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.663263. eCollection 2021. Front Oncol. 2021. PMID: 34123820 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Estrogen receptor on the move: cistromic plasticity and its implications in breast cancer. Mayayo-Peralta I, Prekovic S, Zwart W. Mol Aspects Med. 2021;78:100939. - PubMed
-
- Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Laversanne M, Soerjomataram I, Jemal A, Bray F. CA Cancer J Clin. 2021;71:209–249. - PubMed
-
- Genomic characterization of metastatic breast cancers. Bertucci F, Ng CK, Patsouris A, et al. Nature. 2019;569:560–564. - PubMed
-
- Immune checkpoint inhibitors: Key trials and an emerging role in breast cancer. Gaynor N, Crown J, Collins DM. Semin Cancer Biol. 2022;79:44–57. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
