Evaluation of spine disorders using high contrast imaging of the cartilaginous endplate
- PMID: 38860112
- PMCID: PMC11163041
- DOI: 10.3389/fphys.2024.1394189
Evaluation of spine disorders using high contrast imaging of the cartilaginous endplate
Abstract
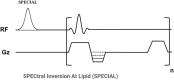
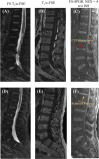
Introduction: Many spine disorders are caused by disc degeneration or endplate defects. Because nutrients entering the avascular disc are channeled through the cartilaginous endplate (CEP), structural and compositional changes in the CEP may block this solute channel, thereby hindering disc cell function. Therefore, imaging the CEP region is important to improve the diagnostic accuracy of spine disorders. Methods: A clinically available T1-weighted and fat-suppressed spoiled gradient recalled-echo (FS-SPGR) sequence was optimized for high-contrast CEP imaging, which utilizes the short T1 property of the CEP. The FS-SPGR scans with and without breath-hold were performed for comparison on healthy subjects. Then, the FS-SPGR sequence which produced optimal image quality was employed for patient scans. In this study, seven asymptomatic volunteers and eight patients with lower back pain were recruited and scanned on a 3T whole-body MRI scanner. Clinical T2-weighted fast spin-echo (T2w-FSE) and T1-weighted FSE (T1w-FSE) sequences were also scanned for comparison. Results: For the asymptomatic volunteers, the FS-SPGR scans under free breathing conditions with NEX = 4 showed much higher contrast-to-noise ratio values between the CEP and bone marrow fat (BMF) (CNRCEP-BMF) (i.e., 7.8 ± 1.6) and between the CEP and nucleus pulposus (NP) (CNRCEP-NP) (i.e., 6.1 ± 1.2) compared to free breathing with NEX = 1 (CNRCEP-BMF: 4.0 ± 1.1 and CNRCEP-NP: 2.5 ± 0.9) and breath-hold condition with NEX = 1 (CNRCEP-BMF: 4.2 ± 1.3 and CNRCEP-NP: 2.8 ± 1.3). The CEP regions showed bright linear signals with high contrast in the T1-weighted FS-SPGR images in the controls, while irregularities of the CEP were found in the patients. Discussion: We have developed a T1-weighted 3D FS-SPGR sequence to image the CEP that is readily translatable to clinical settings. The proposed sequence can be used to highlight the CEP region and shows promise for the detection of intervertebral disc abnormalities.
Keywords: CEP; contrast enhancement; degenerations; spine disorders; spine imaging.
Copyright © 2024 Athertya, Statum, Chen, Du, Shin, Jerban, Chung, Chang and Ma.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest. The authors declared that they were an editorial board member of Frontiers, at the time of submission. This had no impact on the peer review process and the final decision.
Figures
Similar articles
-
High contrast cartilaginous endplate imaging in spine using three dimensional dual-inversion recovery prepared ultrashort echo time (3D DIR-UTE) sequence.Skeletal Radiol. 2024 May;53(5):881-890. doi: 10.1007/s00256-023-04503-4. Epub 2023 Nov 8. Skeletal Radiol. 2024. PMID: 37935923 Free PMC article.
-
MarkVCID cerebral small vessel consortium: II. Neuroimaging protocols.Alzheimers Dement. 2021 Apr;17(4):716-725. doi: 10.1002/alz.12216. Epub 2021 Jan 21. Alzheimers Dement. 2021. PMID: 33480157 Free PMC article.
-
The "horizon gray band" represents normal nucleus pulposus cells condense rather than intervertebral disc degeneration signal.Int J Surg. 2025 Jul 1;111(7):4339-4353. doi: 10.1097/JS9.0000000000002532. Epub 2025 May 26. Int J Surg. 2025. PMID: 40422293
-
Signs and symptoms to determine if a patient presenting in primary care or hospital outpatient settings has COVID-19.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 20;5(5):CD013665. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013665.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 35593186 Free PMC article.
-
The Black Book of Psychotropic Dosing and Monitoring.Psychopharmacol Bull. 2024 Jul 8;54(3):8-59. Psychopharmacol Bull. 2024. PMID: 38993656 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Qualitative and Quantitative MR Imaging of the Cartilaginous Endplate: A Review.J Magn Reson Imaging. 2025 Apr;61(4):1552-1571. doi: 10.1002/jmri.29562. Epub 2024 Aug 20. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2025. PMID: 39165086 Review.
-
Multimodal learning for enhanced SPECT/CT imaging in sports injury diagnosis.Front Physiol. 2025 Jul 29;16:1605426. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2025.1605426. eCollection 2025. Front Physiol. 2025. PMID: 40800735 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Athertya J. S., Lo J., Chen X., Hyun S., Bhavsimran S., Malhi S., et al. (2023). High contrast cartilaginous endplate imaging in spine using three dimensional dual - inversion recovery prepared ultrashort echo time (3D DIR - UTE) sequence. Skelet. Radiol. 53, 881–890. 10.1007/s00256-023-04503-4 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Athertya J. S., Lombardi A. F., Wong J., Jang H., Jerban S., Du J., et al. (2022) Quantitative MR imaging of whole intervertebral disc: a pre-clinical sample study. ISMRM.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

