Identification of molecular interactions of pesticides with keratinase for their potential to inhibit keratin biodegradation
- PMID: 38860143
- PMCID: PMC11162408
- DOI: 10.1007/s40203-024-00229-w
Identification of molecular interactions of pesticides with keratinase for their potential to inhibit keratin biodegradation
Abstract
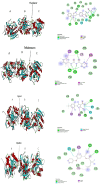
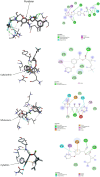
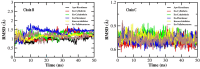
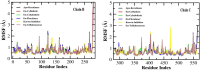
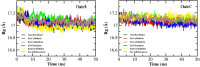
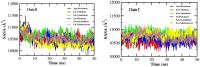
The recalcitrant, fibrous protein keratin is found in the outermost layer of vertebrate skin, feathers, hair, horn, and hooves. Approximately, 10 million tons of keratin wastes are produced annually worldwide, of which around 8.5 million tons are from feather wastes. The biodegradation of keratin has been a challenge due to the lack of understanding of biological parameters that modulate the process. Few soil-borne microbes are capable of producing keratinase enzyme which has the potential to degrade the hard keratin. However, various pesticides are abundantly used for the management of poultry farms and reports suggest the presence of the pesticide residues in feather. Hence, it was hypothesized that pesticides would interact with the substrate-binding or allosteric sites of the keratinase enzyme and interferes with the keratin-degradation process. In the present study, molecular interactions of 20 selected pesticides with the keratinase enzyme were analyzed by performing molecular docking. In blind docking, 14 out of 20 pesticides showed higher inhibitory potential than the known inhibitor phenylmethylsulfonyl flouride, all of which exhibited higher inhibitory potential in site-specific docking. The stability and strength of the protein complexes formed by the top best potential pesticides namely fluralaner, teflubenzuron, cyhalothrin, and cyfluthrin has been further validated by molecular dynamic simulation studies. The present study is the first report for the preliminary investigation of the keratinase-inhibitory potential of pesticides and highlights the plausible role of these pesticides in hindering the biological process of keratin degradation and thereby their contribution in environmental pollution.
Graphical abstract: Illustration depicting the hypothesis, experimental procedure, and the resultant keratinase-inhibitory potential of selected pesticides.
Keywords: Blind docking; Hydrogen bond; Keratinase; Molecular dynamic simulation; Pesticide; Site-specific docking.
© The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer-Verlag GmbH Germany, part of Springer Nature 2024. Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interestAuthors disclosed no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Sustainable production, biochemical and molecular characterization of thermo-and-solvent stable alkaline serine keratinase from novel Bacillus pumilus AR57 for promising poultry solid waste management.Int J Biol Macromol. 2020 Nov 15;163:135-146. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2020.06.219. Epub 2020 Jun 29. Int J Biol Macromol. 2020. PMID: 32615225
-
Biodegradation of Keratin Waste by Bacillus velezensis HFS_F2 through Optimized Keratinase Production Medium.Curr Microbiol. 2024 May 18;81(7):179. doi: 10.1007/s00284-024-03699-5. Curr Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 38761211
-
Directed evolution driving the generation of an efficient keratinase variant to facilitate the feather degradation.Bioresour Bioprocess. 2022 Apr 4;9(1):38. doi: 10.1186/s40643-022-00524-4. Bioresour Bioprocess. 2022. PMID: 38647843 Free PMC article.
-
Current Understanding of Feather Keratin and Keratinase and Their Applications in Biotechnology.Biochem Res Int. 2025 Apr 22;2025:6619273. doi: 10.1155/bri/6619273. eCollection 2025. Biochem Res Int. 2025. PMID: 40308531 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Structure, Application, and Biochemistry of Microbial Keratinases.Front Microbiol. 2021 Jun 23;12:674345. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2021.674345. eCollection 2021. Front Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 34248885 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Abdel-Fattah AM, El-Gamal MS, Ismail SA, Emran MA, Hashem AM. Journal of Genetic Engineering and Biotechnology Biodegradation of feather waste by keratinase produced from newly isolated Bacillus licheniformis ALW1. J Genet Eng Biotechnol. 2018;16(2):311–318. doi: 10.1016/j.jgeb.2018.05.005. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bagewadi ZK, Mulla SI, Ninnekar HZ. Response surface methodology based optimization of keratinase production from Trichoderma harzianum isolate HZN12 using chicken feather waste and its application in dehairing of hide. J Environ Chem Eng. 2018;6(4):4828–4839. doi: 10.1016/j.jece.2018.07.007. - DOI
-
- Banerjee A, Sahoo DK, Thatoi H, Pati BR, Mondal KC, Sen A, Mohapatra PK, Das. Structural characterization and active site prediction of bacterial keratinase through molecular docking. J Bioinform. 2014;1(November):67–82.
-
- Bohacz J, Korni T, Kitowski I, Ciesielska A (2020) International Biodeterioration & Biodegradation Degradation of chicken feathers by Aphanoascus keratinophilus and Chrysosporium tropicum strains from pellets of predatory birds and its practical aspect, 151(April). 10.1016/j.ibiod.2020.104968
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

