Association of dietary inflammatory index with immune-inflammatory biomarkers in rheumatoid arthritis patients: results from NHANES 1999-2018
- PMID: 38860155
- PMCID: PMC11163113
- DOI: 10.3389/fnut.2024.1353964
Association of dietary inflammatory index with immune-inflammatory biomarkers in rheumatoid arthritis patients: results from NHANES 1999-2018
Abstract
Background: Synovial inflammation is the main reason for joint damage in patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA). Diet is recognized as one of the therapeutic strategies to control the inflammatory activity in RA. However, few studies have investigated the association between diet and immune-inflammatory biomarkers in RA patients. Our study aims to examine the correlation between dietary inflammatory potential and systemic immune-inflammation Index (SII), neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio (NLR), platelet-lymphocyte ratio (PLR), and lymphocyte-monocyte ratio (LMR) in the RA population.
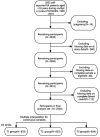
Materials and methods: The National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) was the data source utilized in this study, spanning from 1999 to 2018. The study encompassed 2,500 RA participants in total. The dietary inflammatory potential was calculated by the dietary inflammation index (DII) score based on dietary recall interviews. The generalized multiple linear regression analyses were used to evaluate the relationship between DII and immune-inflammatory markers. Furthermore, subgroup analyses and restricted cubic spline models were performed.
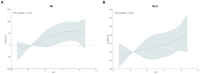
Results: After full adjustments, there were significant positive correlations between DII levels and SII/NLR in RA patients (SII, β: 14.82, 95% CI: 5.14-24.50, p = 0.003; NLR, β: 0.04, 95% CI: 0.01-0.08, p = 0.005). It was noteworthy that inconsistent results were observed in the association between DII and SII as well as NLR in subgroups of red blood cell levels (Interaction p-value <0.001).
Conclusion: Pro-inflammatory dietary status in the RA population is significantly positively correlated with SII and NLR, influenced by variations in red blood cell levels.
Keywords: NHANES; dietary inflammatory index; lymphocyte-monocyte ratio; neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio; platelet-lymphocyte ratio; rheumatoid arthritis; systemic immune inflammation index.
Copyright © 2024 Lu, Xie, Shen, Wu and Feng.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Inflammatory markers are associated with infertility prevalence: a cross-sectional analysis of the NHANES 2013-2020.BMC Public Health. 2024 Jan 18;24(1):221. doi: 10.1186/s12889-024-17699-4. BMC Public Health. 2024. PMID: 38238731 Free PMC article.
-
Association of systemic immune biomarkers with metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease: a cross-sectional study of NHANES 2007-2018.Front Nutr. 2024 Sep 4;11:1415484. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2024.1415484. eCollection 2024. Front Nutr. 2024. PMID: 39296508 Free PMC article.
-
Systemic immune-inflammatory biomarkers (SII, NLR, PLR and LMR) linked to non-alcoholic fatty liver disease risk.Front Immunol. 2024 Feb 28;15:1337241. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1337241. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38481995 Free PMC article.
-
Application Value of Platelet-to-Lymphocyte Ratio as a Novel Indicator in Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Review Based on Clinical Evidence.J Inflamm Res. 2024 Oct 23;17:7607-7617. doi: 10.2147/JIR.S477262. eCollection 2024. J Inflamm Res. 2024. PMID: 39464342 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Diet as a Risk Factor for Rheumatoid Arthritis.Cureus. 2023 May 20;15(5):e39273. doi: 10.7759/cureus.39273. eCollection 2023 May. Cureus. 2023. PMID: 37378145 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Association of dietary inflammatory index and systemic inflammatory markers with mortality risk in depressed adults: a mediation analysis of NHANES data.Front Nutr. 2024 Dec 11;11:1472616. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2024.1472616. eCollection 2024. Front Nutr. 2024. PMID: 39723161 Free PMC article.
-
The relationship between low-carbohydrate diet score, dietary macronutrient intake, and rheumatoid arthritis: results from NHANES 2011-2016.Clin Rheumatol. 2025 Jan;44(1):171-182. doi: 10.1007/s10067-024-07269-9. Epub 2024 Dec 16. Clin Rheumatol. 2025. PMID: 39680261
-
The impact of carbohydrate quality on gut health: Insights from the NHANES.PLoS One. 2025 Feb 13;20(2):e0315795. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0315795. eCollection 2025. PLoS One. 2025. PMID: 39946401 Free PMC article.
-
Relationship Between Serum Interleukin-6 Levels, Systemic Immune-Inflammation Index, and Other Biomarkers Across Different Rheumatoid Arthritis Severity Levels.Cureus. 2024 Oct 24;16(10):e72334. doi: 10.7759/cureus.72334. eCollection 2024 Oct. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 39469275 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

