Primary 3-Month Outcomes of a Double-Blind Randomized Prospective Study (The QUEST Study) Assessing Effectiveness and Safety of Novel High-Frequency Electric Nerve Block System for Treatment of Post-Amputation Pain
- PMID: 38860215
- PMCID: PMC11164212
- DOI: 10.2147/JPR.S463727
Primary 3-Month Outcomes of a Double-Blind Randomized Prospective Study (The QUEST Study) Assessing Effectiveness and Safety of Novel High-Frequency Electric Nerve Block System for Treatment of Post-Amputation Pain
Abstract
Purpose: This multicenter, randomized, double-blinded, active sham-controlled pivotal study was designed to assess the efficacy and safety of high-frequency nerve block treatment for chronic post-amputation and phantom limb pain.
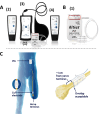
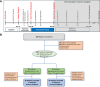
Patients and methods: QUEST enrolled 180 unilateral lower-limb amputees with severe post-amputation pain, 170 of whom were implanted with the Altius device, were randomized 1:1 to active-sham or treatment groups and reached the primary endpoint. Responders were those subjects who received ≥50% pain relief 30 min after treatment in ≥50% of their self-initiated treatment sessions within the 3-month randomized period. Differences between the active treatment and sham control groups as well as numerous secondary outcomes were determined.
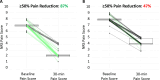
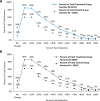
Results: At 30-min, (primary outcome), 24.7% of the treatment group were responders compared to 7.1% of the control group (p=0.002). At 120-minutes following treatment, responder rates were 46.8% in the Treatment group and 22.2% in the Control group (p=0.001). Improvement in Brief Pain Inventory interference score of 2.3 ± 0.29 was significantly greater in treatment group than the 1.3 ± 0.26-point change in the Control group (p = 0.01). Opioid usage, although not significantly different, trended towards a greater reduction in the treatment group than in the control group. The incidence of adverse events did not differ significantly between the treatment and control groups.
Conclusion: The primary outcomes of the study were met, and the majority of Treatment patients experienced a substantial improvement in PAP (regardless of meeting the study definition of a responder). The significant in PAP was associated with significantly improved QOL metrics, and a trend towards reduced opioid utilization compared to Control. These data indicate that Altius treatment represents a significant therapeutic advancement for lower-limb amputees suffering from chronic PAP.
Keywords: high-frequency nerve block; neuromodulation; peripheral nerve stimulation; phantom limb pain; post-amputation pain.
© 2024 Kapural et al.
Conflict of interest statement
Dr Leonardo Kapural reports grants and/or personal fees from Nalu, Biotronik, Saluda, Nevro, Presidio Medical, and Medtronic. Dr Erika Petersen reports grants and/or personal fees from Biotronik, Medtronic Neuromodulation, Nevro, Presidio Medical, Saluda, and SPR, outside the submitted work. Dr Jason Schwalb reports grants from Medtronic, SetPoint, Nevro, MeiraGTX; salary support for role as co-director of the Michigan Spine Surgery Improvement Collaborative, paid directly to employer from Blue Cross Blue Shield of Michigan, outside the submitted work. Dr Maged Guirguis reports personal fees from Nevro, Saluda Medical, Averitas Pharm, Pacira Medical, Boston Scientific, Abbott, Painteq Medical, outside the submitted work. The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Multicenter, Double-Blinded, Randomized, Active-Sham Controlled Clinical Study Design to Assess the Safety and Effectiveness of a Novel High Frequency Electric Nerve Block System in the Treatment of Post-Amputation Pain (The QUEST Study).J Pain Res. 2022 Jun 3;15:1623-1631. doi: 10.2147/JPR.S353674. eCollection 2022. J Pain Res. 2022. PMID: 35685299 Free PMC article.
-
Long-Term Treatment of Chronic Postamputation Pain With Bioelectric Nerve Block: Twelve-Month Results of the Randomized, Double-Blinded, Cross-Over QUEST Study.Neuromodulation. 2024 Dec;27(8):1383-1392. doi: 10.1016/j.neurom.2024.08.010. Epub 2024 Sep 24. Neuromodulation. 2024. PMID: 39320284 Clinical Trial.
-
External Concurrent Occipital and Trigeminal Neurostimulation Relieves Migraine Headache: A Prospective, Randomized, Double-Blind, Sham-Controlled Trial.Pain Ther. 2022 Sep;11(3):907-922. doi: 10.1007/s40122-022-00394-w. Epub 2022 Jun 4. Pain Ther. 2022. PMID: 35661128 Free PMC article.
-
Prevalence and incidence of phantom limb pain, phantom limb sensations and telescoping in amputees: A systematic rapid review.Eur J Pain. 2021 Jan;25(1):23-38. doi: 10.1002/ejp.1657. Epub 2020 Sep 28. Eur J Pain. 2021. PMID: 32885523 Review.
-
Transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation (TENS) for chronic pain - an overview of Cochrane Reviews.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2019 Feb 19;2(2):CD011890. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011890.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2019. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2019 Apr 03;4:CD011890. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011890.pub3. PMID: 30776855 Free PMC article. Updated.
Cited by
-
Review of Guidelines for Implantable Peripheral Nerve Stimulation (PNS) in the Management of Chronic Pain.Curr Pain Headache Rep. 2025 May 23;29(1):89. doi: 10.1007/s11916-025-01397-w. Curr Pain Headache Rep. 2025. PMID: 40410617 Review.
-
Stability of sputtered iridium oxide neural microelectrodes under kilohertz frequency pulsed stimulation.J Neural Eng. 2024 Nov 28;21(6):10.1088/1741-2552/ad9404. doi: 10.1088/1741-2552/ad9404. J Neural Eng. 2024. PMID: 39556962
-
Altius electrical nerve stimulation for post-amputation pain treatment: a comprehensive review.Pain Manag. 2025 Apr;15(4):183-189. doi: 10.1080/17581869.2025.2473873. Epub 2025 Feb 28. Pain Manag. 2025. PMID: 40022501 Review.
References
-
- Caruso M, Harrington S. Prevalence of limb loss and limb difference in the United States: implications for public policy. White Paper. Avalere and Amputation Coalition; 2024.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

