Unmet Needs in Darier's Disease from a Patient's Perspective: Lessons Learnt from the German Registry
- PMID: 38860622
- PMCID: PMC11181922
- DOI: 10.2340/actadv.v104.19663
Unmet Needs in Darier's Disease from a Patient's Perspective: Lessons Learnt from the German Registry
Abstract
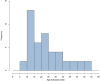
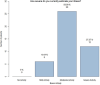
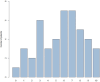
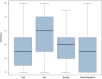
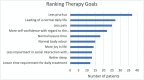
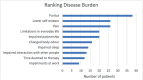
The MDHHgermany registry was initiated to characterize the "real-life" situation of affected individuals with Darier's disease (DD; Morbus Darier, MD) and Hailey-Hailey disease (HH), including their treatment and healthcare. To gain deeper insights into medical care of patients with DD, various aspects such as demographics, subjective symptoms, patient satisfaction with medical care, past and current therapies were explored. Patients with diagnosed DD were included. Subjective symptoms such as itch, pain and burning sensation were assessed. Individual therapy goals were recorded and patients assessed previous/current therapies along with satisfaction of medical care and treatment. A total of 55 patients were recruited; 47 patients were eligible for the analysis. Pruritus was rated the most bothersome symptom. Some 42.6% had not received systemic treatment so far or systemic therapies were rated ineffective (32.6%). Most commonly oral retinoids were prescribed, followed by corticosteroids. Patient satisfaction with medical care and treatment proved to be mediocre. This "real-life" data show an alarming unmet need regarding patients' satisfaction with medical care and treatment, evidenced by the reported lack of disease control. Further studies and interventions are needed to improve the spectrum of available therapies. MDHHgermany provides a foundational platform for future clinical trials, epidemiological studies, and pathophysiological analyses.
Conflict of interest statement
D.R. has received research grants, honoraria as lecturer and/or consultant, and/or travel grants from Eli Lilly, Novartis, and Pfizer. L.H. has no conflicts of interest to be noted. T.B. has no conflicts of interest to be noted. E.S. has no conflicts of interest to be noted. S.H. has no conflicts of interest to be noted. A.Z. has no conflicts of interest to be noted.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Patients' perspective, quality of life and treatment goals in Hailey-Hailey disease: Lessons learned from the German National Registry.J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2024 Feb;38(2):419-429. doi: 10.1111/jdv.19583. Epub 2023 Nov 21. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2024. PMID: 37863661
-
A case of bullous Darier's disease histologically mimicking Hailey-Hailey disease.Dermatol Online J. 2007 Jul 13;13(3):28. Dermatol Online J. 2007. PMID: 18328222
-
Clinical improvement in Darier's disease with photodynamic therapy.Australas J Dermatol. 2010 Feb;51(1):32-5. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-0960.2009.00589.x. Australas J Dermatol. 2010. PMID: 20148839
-
Darier-White disease: a review of the clinical features in 163 patients.J Am Acad Dermatol. 1992 Jul;27(1):40-50. doi: 10.1016/0190-9622(92)70154-8. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1992. PMID: 1619075 Review.
-
Dyskeratosis follicularis disease: case reports and review of the literature.J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2005 Jan;19(1):114-7. doi: 10.1111/j.1468-3083.2004.01096.x. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2005. PMID: 15649206 Review.
Cited by
-
Pruritus and Neuropsychiatric Symptoms Among Patients with Darier Disease-An Overlooked and Interconnected Challenge.J Clin Med. 2025 Mar 8;14(6):1818. doi: 10.3390/jcm14061818. J Clin Med. 2025. PMID: 40142630 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Cooper SM, Burge SM. Darier’s disease: epidemiology, pathophysiology, and management. Am J Clin Dermatol 2003; 4: 97–105. - PubMed
-
- Rogner DF, Lammer J, Zink A, Hamm H. Darier and Hailey-Hailey disease: update 2021. J Dtsch Dermatol Ges 2021; 19: 1478–1501. - PubMed
-
- Miyauchi Y, Daiho T, Yamasaki K, Takahashi H, Ishida-Yamamoto A, Danko S, et al. . Comprehensive analysis of expression and function of 51 sarco(endo)plasmic reticulum Ca2+-ATPase mutants associated with Darier disease. J Biol Chem 2006; 281: 22882–22895. - PubMed
-
- Sakuntabhai A, Dhitavat J, Burge S, Hovnanian A. Mosaicism for ATP2A2 mutations causes segmental Darier’s disease. J Invest Dermatol 2000; 115: 1144–1147. - PubMed
-
- Burge SM, Wilkinson JD. Darier-White disease: a review of the clinical features in 163 patients. J Am Acad Dermatol 1992; 27: 40–50. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

