Building Block-Centric Approach to DNA-Encoded Library Design
- PMID: 38860710
- PMCID: PMC11200258
- DOI: 10.1021/acs.jcim.4c00232
Building Block-Centric Approach to DNA-Encoded Library Design
Abstract
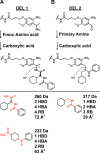
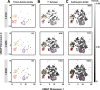
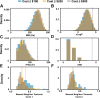
DNA-encoded library technology grants access to nearly infinite opportunities to explore the chemical structure space for drug discovery. Successful navigation depends on the design and synthesis of libraries with appropriate physicochemical properties (PCPs) and structural diversity while aligning with practical considerations. To this end, we analyze combinatorial library design constraints including the number of chemistry cycles, bond construction strategies, and building block (BB) class selection in pursuit of ideal library designs. We compare two-cycle library designs (amino acid + carboxylic acid, primary amine + carboxylic acid) in the context of PCPs and chemical space coverage, given different BB selection strategies and constraints. We find that broad availability of amines and acids is essential for enabling the widest exploration of chemical space. Surprisingly, cost is not a driving factor, and virtually, the same chemical space can be explored with "budget" BBs.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare the following competing financial interest(s): D.L.M. serves on the scientific advisory boards of Anagenex and OpenEye Scientific Software, Cadence Molecular Sciences. He is also an Open Science Fellow with Psivant.
Figures



References
-
- Clark M. A.; Acharya R. A.; Arico-Muendel C. C.; Belyanskaya S. L.; Benjamin D. R.; Carlson N. R.; Centrella P. A.; Chiu C. H.; Creaser S. P.; Cuozzo J. W.; Davie C. P.; Ding Y.; Franklin G. J.; Franzen K. D.; Gefter M. L.; Hale S. P.; Hansen N. J. V.; Israel D. I.; Jiang J.; Kavarana M. J.; Kelley M. S.; Kollmann C. S.; Li F.; Lind K.; Mataruse S.; Medeiros P. F.; Messer J. A.; Myers P.; O’Keefe H.; Oliff M. C.; Rise C. E.; Satz A. L.; Skinner S. R.; Svendsen J. L.; Tang L.; van Vloten K.; Wagner R. W.; Yao G.; Zhao B.; Morgan B. A.; Van Vloten K.; Wagner R. W.; Yao G.; Zhao B.; Morgan B. A.; van Vloten K.; Wagner R. W.; Yao G.; Zhao B.; Morgan B. A. Design, Synthesis and Selection of DNA-Encoded Small-Molecule Libraries. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2009, 5, 647–654. 10.1038/nchembio.211. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Harris P. A.; King B. W.; Bandyopadhyay D.; Berger S. B.; Campobasso N.; Capriotti C. A.; Cox J. A.; Dare L.; Dong X.; Finger J. N.; Grady L. C.; Hoffman S. J.; Jeong J. U.; Kang J.; Kasparcova V.; Lakdawala A. S.; Lehr R.; McNulty D. E.; Nagilla R.; Ouellette M. T.; Pao C. S.; Rendina A. R.; Schaeffer M. C.; Summerfield J. D.; Swift B. A.; Totoritis R. D.; Ward P.; Zhang A.; Zhang D.; Marquis R. W.; Bertin J.; Gough P. J. DNA-Encoded Library Screening Identifies Benzo[b] [1,4]oxazepin-4-ones as Highly Potent and Monoselective Receptor Interacting Protein 1 Kinase Inhibitors. J. Med. Chem. 2016, 59, 2163–2178. 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.5b01898. - DOI - PubMed

