PAI-1 deficiency drives pulmonary vascular smooth muscle remodeling and pulmonary hypertension
- PMID: 38860847
- PMCID: PMC11444499
- DOI: 10.1152/ajplung.00110.2024
PAI-1 deficiency drives pulmonary vascular smooth muscle remodeling and pulmonary hypertension
Abstract
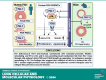
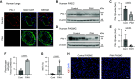
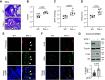
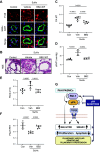
Pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH) is a progressive disease characterized by vasoconstriction and remodeling of small pulmonary arteries (PAs). Central to the remodeling process is a switch of pulmonary vascular cells to a proliferative, apoptosis-resistant phenotype. Plasminogen activator inhibitors-1 and -2 (PAI-1 and PAI-2) are the primary physiological inhibitors of urokinase-type and tissue-type plasminogen activators (uPA and tPA), but their roles in PAH are unsettled. Here, we report that: 1) PAI-1, but not PAI-2, is deficient in remodeled small PAs and in early-passage PA smooth muscle and endothelial cells (PASMCs and PAECs) from subjects with PAH compared with controls; 2) PAI-1-/- mice spontaneously develop pulmonary vascular remodeling associated with upregulation of mTORC1 signaling, pulmonary hypertension (PH), and right ventricle (RV) hypertrophy; and 3) pharmacological inhibition of uPA in human PAH PASMCs suppresses proproliferative mTORC1 and SMAD3 signaling, restores PAI-1 levels, reduces proliferation, and induces apoptosis in vitro, and prevents the development of SU5416/hypoxia-induced PH and RV hypertrophy in vivo in mice. These data strongly suggest that downregulation of PAI-1 in small PAs promotes vascular remodeling and PH due to unopposed activation of uPA and consequent upregulation of mTOR and transforming growth factor-β (TGF-β) signaling in PASMCs, and call for further studies to determine the potential benefits of targeting the PAI-1/uPA imbalance to attenuate and/or reverse pulmonary vascular remodeling and PH.NEW & NOTEWORTHY This study identifies a novel role for the deficiency of plasminogen activator inhibitor (PAI)-1 and resultant unrestricted uPA activity in PASMC remodeling and PH in vitro and in vivo, provides novel mechanistic link from PAI-1 loss through uPA-induced Akt/mTOR and TGFβ-Smad3 upregulation to pulmonary vascular remodeling in PH, and suggests that inhibition of uPA to rebalance the uPA-PAI-1 tandem might provide a novel approach to complement current therapies used to mitigate this pulmonary vascular disease.
Keywords: plasminogen activator inhibitor (PAI-1); pulmonary hypertension; urokinase PA (uPA).
Conflict of interest statement
No conflicts of interest, financial or otherwise, are declared by the authors.
Figures

Update of
-
PAI-1 Deficiency Drives Pulmonary Vascular Smooth Muscle Remodeling and Pulmonary Hypertension.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2023 Sep 22:2023.09.21.558893. doi: 10.1101/2023.09.21.558893. bioRxiv. 2023. Update in: Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2024 Sep 1;327(3):L319-L326. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.00110.2024. PMID: 37790328 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
-
- Pullamsetti SS, Savai R, Seeger W, Goncharova EA. Translational advances in the field of pulmonary hypertension. From cancer biology to new pulmonary arterial hypertension therapeutics. Targeting cell growth and proliferation signaling hubs. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 195: 425–437, 2017. doi: 10.1164/rccm.201606-1226PP. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Gupta KK, Donahue DL, Sandoval-Cooper MJ, Castellino FJ, Ploplis VA. plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 protects mice against cardiac fibrosis by inhibiting urokinase-type plasminogen activator-mediated plasminogen activation. Sci Rep 7: 365, 2017. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-00418-y. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Lijnen HR. Plasmin and matrix metalloproteinases in vascular remodeling. Thromb Haemost 86: 324–333, 2001. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 HL159256/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01HL150638/HHS | NIH | National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (NHLBI)
- R01 HL139881/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- Nina Ireland Program for Lung Health/UCSF | Department of Medicine, University of California, San Francisco (UCSF Department of Medicine)
- R01 HL141462/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL166932/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R35HL150698/HHS | NIH | National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (NHLBI)
- R24 HL123767/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- I01 CX002011/CX/CSRD VA/United States
- R01 HL130261/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01HL130261/HHS | NIH | National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (NHLBI)
- R01HL166932/HHS | NIH | National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (NHLBI)
- LAM0139P07-19/LAM Foundation (TheLAMFoundation)
- R01HL139881/HHS | NIH | National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (NHLBI)
- APP1181179/DHAC | National Health and Medical Research Council (NHMRC)
- TS150032/DOD | USA | MEDCOM | MRDC | U.S. Army Medical Research Acquisition Activity (USAMRAA)
- CX002011/ORD | Clinical Science Research and Development (CSRD)
- Cardiovascular Medical Research and Education Fund (CMREF)
- RO1HL159256/HHS | NIH | National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (NHLBI)
- R01HL172488/HHS | NIH | National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (NHLBI)
- R01 HL150638/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL172488/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- RO1HL141462/HHS | NIH | National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (NHLBI)
- R35 HL150698/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

