The Effect of Endurance Exercise on Semen Quality in Male Athletes: A Systematic Review
- PMID: 38861008
- PMCID: PMC11166609
- DOI: 10.1186/s40798-024-00739-z
The Effect of Endurance Exercise on Semen Quality in Male Athletes: A Systematic Review
Abstract
Background: Endurance exercise has the potential to affect reproductive function, with amenorrhea in female athletes. However, most studies focus on women. Evidence on the association between endurance exercise and male fertility is limited.
Objective: To synthesise existing literature on exercise-induced alterations in semen parameters and to assess the clinical impact on male fertility.
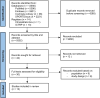
Methods: Studies reporting on the association between semen parameters and endurance exercise in healthy men were eligible. Men attending fertility clinics were excluded. We searched MEDLINE (PubMed), Embase, SPORTDiscus, Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials (CENTRAL), ClinicalTrials.gov and International Clinical Trials Registry Platform (ICTRP) from their inception to May 28th 2022. JBI Critical Appraisal Tool was used to assess the potential risk of bias.
Results: Thirteen studies met inclusion criteria, reporting on 280 subjects. Eight articles reported on endurance runners, three on cyclists and four on triathletes. Four studies did not find any statistically significant sperm alterations. Five reported significant changes in semen parameters, but these were not clinically relevant, as semen parameters remained well above World Health Organisation (WHO) thresholds. Four articles reported a decrease in semen quality with potential clinical consequences as they found a reduced number of sperm cells exhibiting normal morphology in cyclists and triathletes and a greater amount of DNA fragmentation in triathletes.
Conclusion: Endurance exercise can have a negative effect on semen quality, although rarely with a clinically relevant impact on male fertility. Evidence is however limited, with poor quality of the included studies.
Registration: PROSPERO International prospective register of systematic reviews (CRD42022336753).
Keywords: Endurance exercise; Male reproduction; Semen quality.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
None of the authors declare any competing interests with the content of this review.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Sperm DNA fragmentation as a result of ultra-endurance exercise training in male athletes.Andrologia. 2018 Feb;50(1). doi: 10.1111/and.12793. Epub 2017 Mar 15. Andrologia. 2018. PMID: 28295487
-
Exercise and male factor infertility.Sports Med. 1993 Mar;15(3):146-69. doi: 10.2165/00007256-199315030-00002. Sports Med. 1993. PMID: 8451548 Review.
-
Relationship between leukocytospermia, reproductive potential after assisted reproductive technology, and sperm parameters: a systematic review and meta-analysis of case-control studies.Andrology. 2020 Jan;8(1):125-135. doi: 10.1111/andr.12662. Epub 2019 Jun 28. Andrology. 2020. PMID: 31250986
-
Sexual function and reproduction can be impaired in men with rheumatic diseases: A systematic review.Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2020 Jun;50(3):557-573. doi: 10.1016/j.semarthrit.2020.02.002. Epub 2020 Feb 14. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2020. PMID: 32165034
-
Beyond the black stump: rapid reviews of health research issues affecting regional, rural and remote Australia.Med J Aust. 2020 Dec;213 Suppl 11:S3-S32.e1. doi: 10.5694/mja2.50881. Med J Aust. 2020. PMID: 33314144
Cited by
-
The Influence of an Intense Training Regime in Professional and Non-Professional Athletes on Semen Parameters: A Systematic Review.J Clin Med. 2025 Jan 1;14(1):201. doi: 10.3390/jcm14010201. J Clin Med. 2025. PMID: 39797284 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effects of sport disciplines on offspring sex ratio in elite athletes: an observational study.Sci Rep. 2025 Jul 1;15(1):21677. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-05445-8. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40595831 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous