A human STAT3 gain-of-function variant drives local Th17 dysregulation and skin inflammation in mice
- PMID: 38861030
- PMCID: PMC11167377
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.20232091
A human STAT3 gain-of-function variant drives local Th17 dysregulation and skin inflammation in mice
Abstract
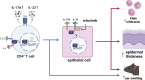
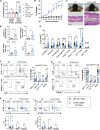
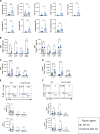
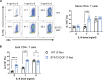
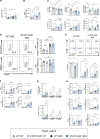
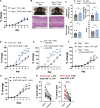
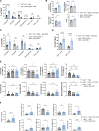
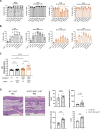
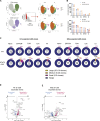
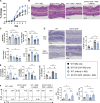
Germline gain-of-function (GOF) variants in STAT3 cause an inborn error of immunity associated with early-onset poly-autoimmunity and immune dysregulation. To study tissue-specific immune dysregulation, we used a mouse model carrying a missense variant (p.G421R) that causes human disease. We observed spontaneous and imiquimod (IMQ)-induced skin inflammation associated with cell-intrinsic local Th17 responses in STAT3 GOF mice. CD4+ T cells were sufficient to drive skin inflammation and showed increased Il22 expression in expanded clones. Certain aspects of disease, including increased epidermal thickness, also required the presence of STAT3 GOF in epithelial cells. Treatment with a JAK inhibitor improved skin disease without affecting local Th17 recruitment and cytokine production. These findings collectively support the involvement of Th17 responses in the development of organ-specific immune dysregulation in STAT3 GOF and suggest that the presence of STAT3 GOF in tissues is important for disease and can be targeted with JAK inhibition.
© 2024 Toth et al.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosures: B.S. Kim is founder of Klirna Biotech; he has served as a consultant for 23andMe, ABRAX Japan, AbbVie, Almirall, Amagma Therapeutics, Amgen, Arcutis Biotherapeutics, Arena Pharmaceuticals, argenx, AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim, Bristol Myers Squibb, Cara Therapeutics, Clexio Biosciences, Eli Lilly and Company, Escient Pharmaceuticals, Evommune, Galderma, Genentech, GlaxoSmithKline, Granular Therapeutics, Incyte Corporation, Innovaderm Research, Janssen, Kiniksa, LEO Pharma, Maruho, Novartis, Pfizer, Recens Medical, Regeneron Pharmaceuticals, Sanofi, Septerna, Vial, WebMD; he has stock in ABRAX Japan, KliRNA Biotech, Locus Biosciences, and Recens Medical; he holds a patent for the use of JAK1 inhibitors for chronic pruritus; he has a patent pending for the use of JAK inhibitors for interstitial cystitis. He has research grants from AbbVie, Cara Therapeutics, LEO Pharma, and Veradermics. No other disclosures were reported.
Figures





References
-
- Al-Ismaeel, Q. , Neal C.P., Al-Mahmoodi H., Almutairi Z., Al-Shamarti I., Straatman K., Jaunbocus N., Irvine A., Issa E., Moreman C., et al. . 2019. ZEB1 and IL-6/11-STAT3 signalling cooperate to define invasive potential of pancreatic cancer cells via differential regulation of the expression of S100 proteins. Br. J. Cancer. 121:65–75. 10.1038/s41416-019-0483-9 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Barnes, J.L. , Plank M.W., Asquith K., Maltby S., Sabino L.R., Kaiko G.E., Lochrin A., Horvat J.C., Mayall J.R., Kim R.Y., et al. . 2021. T-helper 22 cells develop as a distinct lineage from Th17 cells during bacterial infection and phenotypic stability is regulated by T-bet. Mucosal Immunol. 14:1077–1087. 10.1038/s41385-021-00414-6 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Bovenschen, H.J. , van de Kerkhof P.C., van Erp P.E., Woestenenk R., Joosten I., and Koenen H.J.. 2011. Foxp3+ regulatory T cells of psoriasis patients easily differentiate into IL-17A-producing cells and are found in lesional skin. J. Invest. Dermatol. 131:1853–1860. 10.1038/jid.2011.139 - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- P30 CA91842/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 EB028092/EB/NIBIB NIH HHS/United States
- Division of Intramural Research of the NIAID
- P30 AR048335/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- Siteman Cancer Center
- 1P01AI155393/NH/NIH HHS/United States
- P01 AI155393/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases
- P30 AR073752/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA091842/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- Scleroderma Foundation
- P30DK052574/Washington University
- K12 HD076224/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- St. Louis Children's Hospital
- P30 DK052574/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- P30AR073752/Washington University Rheumatic Diseases Research Resource-based Center
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

