Diagnosis of Sports-Related Concussion Using Symptom Report or Standardized Assessment of Concussion
- PMID: 38861257
- PMCID: PMC11167498
- DOI: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2024.16223
Diagnosis of Sports-Related Concussion Using Symptom Report or Standardized Assessment of Concussion
Abstract
Importance: The Sports Concussion Assessment Tool-5 (SCAT5) has been recommended for concussion evaluation and utilizes both a subjective reported symptom grading scale and objective measures of concussion including a cognitive evaluation: the Standardized Assessment of Concussion (SAC). The SAC includes testing for orientation, immediate memory, concentration, and delayed recall; a 10-word list is used to assess immediate memory and delayed recall.
Objective: To determine the diagnostic accuracy of components of the SCAT5 and to provide a framework for clinical interpretation.
Design, setting, and participants: This prospective case-control study of National Collegiate Athletic Association Division I athletes from any sport was conducted from July 2020 to December 2022 at 4 universities. Athletes completed baseline SCAT5 testing using the 10-word list. When an athlete presented acutely with suspected concussion (sideline or within 2 days), the tests were repeated. If a concussion was diagnosed, a control athlete underwent the same tests. Controls were identified and matched on comorbid conditions, sex and gender, sport, season, and baseline scores. Data analysis was conducted from August to October 2023.
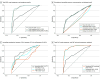
Main outcomes and measures: The primary outcomes were area under the receiver operating characteristic curve (AUC), sensitivity, specificity, positive and negative predictive value, and test-retest reliability of the symptom score; symptom severity score; the total SAC score; and the orientation, immediate memory, concentration, and delayed memory subcomponent scores on the SCAT5 compared with clinical diagnosis of concussion.
Results: Baseline and postinjury data were collected on 92 athletes with concussion and 92 matched control athletes (96 men [52%] and 88 women [48%]; 110 who played a sport other than football [59%]). Diagnostic utility was considered excellent for symptom score (AUC, 0.93; 95% CI, 0.89-0.96) and symptom severity score (AUC, 0.94; 95% CI, 0.90-0.97). An increase of 2 points on the symptom score was associated with a sensitivity of 86% (95% CI, 78%-92%), specificity of 80% (95% CI, 70%-87I%), and positive predictive value of 81% (95% CI, 72%-88%). The total SAC score had poor to fair diagnostic utility (AUC, 0.70; 95% CI, 0.63-0.77); however, 41 athletes with concussion (45%) had a total SAC score at or above their baseline score (ie, within normal limits). The diagnostic utility was poor to fair for immediate memory (AUC, 0.68, 95%CI, 0.61-0.75) and delayed recall (AUC, 0.69; 95% CI, 0.62-0.77) and not useful for orientation (AUC, 0.49; 95% CI, 0.43-0.56) and concentration (AUC, 0.52 95% CI, 0.44-0.61). Test-retest reliability was fair for total SAC and poor for immediate memory and delayed recall, orientation, and concentration.
Conclusions and relevance: In this case-control study of the diagnostic accuracy of reported symptoms and the SAC, reported symptoms were the most accurate indicator of concussion while the 10-word SAC had limited sensitivity. These findings suggest that understanding the properties of the SAC is important when making the diagnosis of concussion.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Utility of VOMS, SCAT3, and ImPACT Baseline Evaluations for Acute Concussion Identification in Collegiate Athletes: Findings From the NCAA-DoD Concussion Assessment, Research and Education (CARE) Consortium.Am J Sports Med. 2022 Mar;50(4):1106-1119. doi: 10.1177/03635465211072261. Epub 2022 Feb 18. Am J Sports Med. 2022. PMID: 35179972
-
Reliability and Validity of the Sport Concussion Assessment Tool-3 (SCAT3) in High School and Collegiate Athletes.Am J Sports Med. 2016 Sep;44(9):2276-85. doi: 10.1177/0363546516648141. Epub 2016 Jun 8. Am J Sports Med. 2016. PMID: 27281276
-
American Medical Society for Sports Medicine position statement: concussion in sport.Br J Sports Med. 2013 Jan;47(1):15-26. doi: 10.1136/bjsports-2012-091941. Br J Sports Med. 2013. PMID: 23243113 Review.
-
SCAT5 Sex Differences: Normative Data, Clinical Thresholds, and Relevance for Identification of Concussion.Arch Clin Neuropsychol. 2022 Oct 19;37(7):1536-1544. doi: 10.1093/arclin/acac007. Arch Clin Neuropsychol. 2022. PMID: 35260877
-
Do Sideline Concussion Assessments Predict Subsequent Neurocognitive Impairment After Sport-Related Concussion?J Athl Train. 2017 Jul;52(7):676-681. doi: 10.4085/1062-6050-52.4.01. Epub 2017 May 23. J Athl Train. 2017. PMID: 28535099 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Clinical Utility of the Sport Concussion Office Assessment Tool 6 (SCOAT6) and Other Select Multidomain Assessments for Subacute Sport-Related Concussion.Sports Med. 2025 Jun 8. doi: 10.1007/s40279-025-02256-9. Online ahead of print. Sports Med. 2025. PMID: 40483661
-
Spontaneous Headshake after a Kinematic Event (SHAAKE): Evaluating the Utility of a Potential New Sign in the Diagnosis of Concussion.Diagnostics (Basel). 2024 Oct 17;14(20):2314. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics14202314. Diagnostics (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39451636 Free PMC article.
-
Validity of the King Devick Test for Acute Diagnosis of Concussion in NCAA Division I Athletes.Sports Health. 2025 Jul 8:19417381251350685. doi: 10.1177/19417381251350685. Online ahead of print. Sports Health. 2025. PMID: 40625038 Free PMC article.
-
Smartphone-Based Pupillometry Using Machine Learning for the Diagnosis of Sports-Related Concussion.Diagnostics (Basel). 2024 Dec 3;14(23):2723. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics14232723. Diagnostics (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39682632 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

