An attenuated lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus vector enhances tumor control in mice partly via IFN-I
- PMID: 38861331
- PMCID: PMC11290963
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI178945
An attenuated lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus vector enhances tumor control in mice partly via IFN-I
Abstract
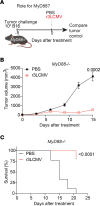
Viral vectors are being used for the treatment of cancer. Yet, their efficacy varies among tumors and their use poses challenges in immunosuppressed patients, underscoring the need for alternatives. We report striking antitumoral effects by a nonlytic viral vector based on attenuated lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus (r3LCMV). We show in multiple tumor models that injection of tumor-bearing mice with this vector results in improved tumor control and survival. Importantly, r3LCMV improved tumor control in immunodeficient Rag1-/- mice and MyD88-/- mice, suggesting that multiple pathways contributed to the antitumoral effects. The antitumoral effects of r3LCMV were also observed when this vector was administered several weeks before tumor challenges, suggesting the induction of trained immunity. Single-cell RNA sequencing analyses, antibody blockade experiments, and knockout models revealed a critical role for host-intrinsic IFN-I in the antitumoral efficacy of r3LCMV vectors. Collectively, these data demonstrate potent antitumoral effects by r3LCMV vectors and unveil multiple mechanisms underlying their antitumoral efficacy.
Keywords: Adaptive immunity; Cancer immunotherapy; Cellular immune response; Immunology; Vaccines.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Replication-attenuated r3LCMV vectors potentiate tumor control via IFN-I.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2023 Dec 8:2023.12.08.570847. doi: 10.1101/2023.12.08.570847. bioRxiv. 2023. PMID: 38106001 Free PMC article. Preprint.
-
Interleukin-27R Signaling Mediates Early Viral Containment and Impacts Innate and Adaptive Immunity after Chronic Lymphocytic Choriomeningitis Virus Infection.J Virol. 2018 May 29;92(12):e02196-17. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02196-17. Print 2018 Jun 15. J Virol. 2018. PMID: 29593047 Free PMC article.
-
IRF9 Prevents CD8+ T Cell Exhaustion in an Extrinsic Manner during Acute Lymphocytic Choriomeningitis Virus Infection.J Virol. 2017 Oct 27;91(22):e01219-17. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01219-17. Print 2017 Nov 15. J Virol. 2017. PMID: 28878077 Free PMC article.
-
Confounding roles for type I interferons during bacterial and viral pathogenesis.Int Immunol. 2013 Dec;25(12):663-9. doi: 10.1093/intimm/dxt050. Epub 2013 Oct 24. Int Immunol. 2013. PMID: 24158954 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Type I interferon during viral infections: multiple triggers for a multifunctional mediator.Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2007;316:337-57. doi: 10.1007/978-3-540-71329-6_16. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2007. PMID: 17969455 Review.
Cited by
-
Delayed reinforcement of costimulation improves the efficacy of mRNA vaccines in mice.J Clin Invest. 2024 Oct 21;134(24):e183973. doi: 10.1172/JCI183973. J Clin Invest. 2024. PMID: 39432667 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of protein boosters on antibody responses.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2025 Feb 11:2025.02.08.637239. doi: 10.1101/2025.02.08.637239. bioRxiv. 2025. PMID: 39990358 Free PMC article. Preprint.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

