Identification of exosomal circSLC26A4 as a liquid biopsy marker for cervical cancer
- PMID: 38861540
- PMCID: PMC11166277
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0305050
Identification of exosomal circSLC26A4 as a liquid biopsy marker for cervical cancer
Abstract
Objective: Circular RNA SLC26A4 (circSLC26A4) functions as an oncogene in the initiation and progression of cervical cancer (CC). However, the clinical role of plasma exosomal circSLC26A4 in CC is poorly known. This study aims to develop an accurate diagnostic method based on circulating exosomal circSLC26A4.
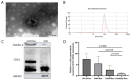
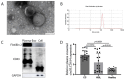
Methods: In this study, exosomal circSLC26A4 derived from CC cell lines (CaSki, SiHa, and HeLa) and human cervical epithelial cells (HcerEpic) was measured and compared using quantitative reverse transcriptase polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR). Additionally, 56 volunteers, including 18 CC patients, 18 cervical high-grade squamous intraepithelial lesion (HSIL) patients, and 20 healthy volunteers, were enrolled. qRT-PCR was also performed to measure the plasma exosomal circSLC26A4 levels in all participants.
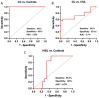
Results: The exosomal circSLC26A4 expression level derived from CC cells was significantly elevated compared to it derived from HcerEpic cells. Plasma exosomal circSLC26A4 levels in CC patients were significantly higher than in healthy women and HSIL patients (P < 0.05). In addition, high plasma exosomal circSLC26A4 expression was positively associated with lymph node metastasis and FIGO stage (all P < 0.05). However, no significant correlation was found between plasma exosomal circSLC26A4 expression and age, intravascular cancerous embolus, and perineural invasion (P > 0.05).
Conclusions: The high exosomal circSLC26A4 expression is closely related to the occurrence of CC. Plasma exosomal circSLC26A4 can be used as a diagnostic marker for CC.
Copyright: © 2024 Tong et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Serum Exosomal lncRNA DLX6-AS1 Is a Promising Biomarker for Prognosis Prediction of Cervical Cancer.Technol Cancer Res Treat. 2021 Jan-Dec;20:1533033821990060. doi: 10.1177/1533033821990060. Technol Cancer Res Treat. 2021. PMID: 33550924 Free PMC article.
-
The expression and clinical significance of serum exosomal-long non-coding RNA DLEU1 in patients with cervical cancer.Ann Med. 2025 Dec;57(1):2442537. doi: 10.1080/07853890.2024.2442537. Epub 2024 Dec 17. Ann Med. 2025. PMID: 39687982 Free PMC article.
-
Appraising the Value of Serum and Serum-Derived Exosomal LncRNA-EXOC7 as a Promising Biomarker in Cervical Cancer.Clin Lab. 2020 Jul 1;66(7). doi: 10.7754/Clin.Lab.2019.191203. Clin Lab. 2020. PMID: 32658426
-
Underlying metastasis mechanism and clinical application of exosomal circular RNA in tumors (Review).Int J Oncol. 2021 Mar;58(3):289-297. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2021.5179. Epub 2021 Jan 28. Int J Oncol. 2021. PMID: 33650643 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Advances in exosome biomarkers for cervical cancer.Cancer Med. 2022 Dec;11(24):4966-4978. doi: 10.1002/cam4.4828. Epub 2022 May 16. Cancer Med. 2022. PMID: 35578572 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Circulating non-coding RNAs as a tool for liquid biopsy in solid tumors.Epigenomics. 2025 Apr;17(5):335-358. doi: 10.1080/17501911.2025.2467021. Epub 2025 Mar 5. Epigenomics. 2025. PMID: 40040488 Review.
-
Diagnostic and Prognostic Significance of Exosomes and Their Components in Patients With Cancers.Cancer Med. 2025 Jan;14(1):e70569. doi: 10.1002/cam4.70569. Cancer Med. 2025. PMID: 39757782 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Liquid biopsy in gynecological cancers: a translational framework from molecular insights to precision oncology and clinical practice.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2025 May 8;44(1):140. doi: 10.1186/s13046-025-03371-1. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2025. PMID: 40340939 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel R L, et al.. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries [J]. CA Cancer J Clin, 2021, 71(3): 209–249. - PubMed
-
- Burness J V, Schroeder J M, Warren J B. Cervical Colposcopy: Indications and Risk Assessment [J]. Am Fam Physician, 2020, 102(1): 39–48. - PubMed

