Case Report: Neurobrucellosis Presenting as Malignancy
- PMID: 38861982
- PMCID: PMC11310615
- DOI: 10.4269/ajtmh.23-0684
Case Report: Neurobrucellosis Presenting as Malignancy
Abstract
Neurobrucellosis, caused by Brucella species, is a zoonotic infection that may involve the central nervous system. Although uncommon, it can manifest as a solitary intracranial mass. We report a case of neurobrucellosis in a 25-year-old woman from Peru who presented with headache, weight loss, and right-side hemiparesis and paresthesia. A contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging scan revealed an intracerebral mass in the left temporal lobe. Serum testing subsequently were positive. Brain biopsy demonstrated non-necrotizing granulomas without malignant cells. Neurobrucellosis should be considered in the differential diagnosis of brain space occupying lesions in endemic countries.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure: The patient’s written consent was obtained. Local committee approval does not apply in this case.
Figures
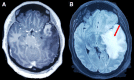
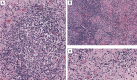
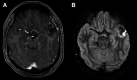
References
-
- Patra S, Kalwaje Eshwara V, Pai AR, Varma M, Mukhopadhyay C, 2020. Evaluation of clinical, diagnostic features and therapeutic outcome of neurobrucellosis: A case series and review of literature. Int J Neurosci 132: 1080–1090. - PubMed
-
- Guven T, Ugurlu K, Ergonul O, Celikbas AK, Gok SE, Comoglu S, Baykam N, Dokuzoguz B, 2013. Neurobrucellosis: Clinical and diagnostic features. Clin Infect Dis 56: 1407–1412. - PubMed
-
- MINSA , 2022. Situación de brucelosis humana en el Perú, una revisión de dat 2009–2018 del sistema HIS–MINSA. Available at: https://www.dge.gob.pe/epipublic/uploads/boletin/boletin_20218.pdf. Accessed 17 September, 2022.
-
- Negrón M, Tiller R, Kharod G, 2024. Brucellosis. CDC Yellow Book 2024: Health Information for International Travel [e-book] New York, NY: Oxford University Press; 1st ed. Available from: https://wwwnc.cdc.gov/travel/yellowbook/2024/infections-diseases/brucell.... Accessed May 11, 2024.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

