Identifying behavioral links to neural dynamics of multifiber photometry recordings in a mouse social behavior network
- PMID: 38861996
- PMCID: PMC11246699
- DOI: 10.1088/1741-2552/ad5702
Identifying behavioral links to neural dynamics of multifiber photometry recordings in a mouse social behavior network
Abstract
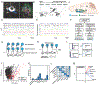
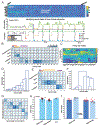
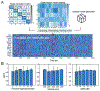
Objective.Distributed hypothalamic-midbrain neural circuits help orchestrate complex behavioral responses during social interactions. Given rapid advances in optical imaging, it is a fundamental question how population-averaged neural activity measured by multi-fiber photometry (MFP) for calcium fluorescence signals correlates with social behaviors is a fundamental question. This paper aims to investigate the correspondence between MFP data and social behaviors.Approach:We propose a state-space analysis framework to characterize mouse MFP data based on dynamic latent variable models, which include a continuous-state linear dynamical system and a discrete-state hidden semi-Markov model. We validate these models on extensive MFP recordings during aggressive and mating behaviors in male-male and male-female interactions, respectively.Main results:Our results show that these models are capable of capturing both temporal behavioral structure and associated neural states, and produce interpretable latent states. Our approach is also validated in computer simulations in the presence of known ground truth.Significance:Overall, these analysis approaches provide a state-space framework to examine neural dynamics underlying social behaviors and reveals mechanistic insights into the relevant networks.
Keywords: dynamical systems; latent variable model; multi-fiber photometry; social behavior network; social behaviors.
© 2024 IOP Publishing Ltd.
Figures



Update of
-
Identifying behavioral links to neural dynamics of multifiber photometry recordings in a mouse social behavior network.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Jan 6:2023.12.25.573308. doi: 10.1101/2023.12.25.573308. bioRxiv. 2024. Update in: J Neural Eng. 2024 Jun 25;21(3). doi: 10.1088/1741-2552/ad5702. PMID: 38234793 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
Similar articles
-
Identifying behavioral links to neural dynamics of multifiber photometry recordings in a mouse social behavior network.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Jan 6:2023.12.25.573308. doi: 10.1101/2023.12.25.573308. bioRxiv. 2024. Update in: J Neural Eng. 2024 Jun 25;21(3). doi: 10.1088/1741-2552/ad5702. PMID: 38234793 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Apr 19;4(4):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 23;5:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub5. PMID: 33871055 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
Uncovering hidden prosocial behaviors underlying aggression motivation in mice and young children.Behav Brain Funct. 2024 Nov 28;20(1):32. doi: 10.1186/s12993-024-00260-z. Behav Brain Funct. 2024. PMID: 39609920 Free PMC article.
-
Immunogenicity and seroefficacy of pneumococcal conjugate vaccines: a systematic review and network meta-analysis.Health Technol Assess. 2024 Jul;28(34):1-109. doi: 10.3310/YWHA3079. Health Technol Assess. 2024. PMID: 39046101 Free PMC article.
-
How lived experiences of illness trajectories, burdens of treatment, and social inequalities shape service user and caregiver participation in health and social care: a theory-informed qualitative evidence synthesis.Health Soc Care Deliv Res. 2025 Jun;13(24):1-120. doi: 10.3310/HGTQ8159. Health Soc Care Deliv Res. 2025. PMID: 40548558
References
-
- Batty E, Whiteway MR, Saxena S, Biderman D, Abe T, et al. BehaveNet: nonlinear embedding and Bayesian neural decoding of behavioral videos. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 33 (NeurIPS’19) (2019).
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
