Disulfidptosis-related lncRNAs signature predicting prognosis and immunotherapy effect in lung adenocarcinoma
- PMID: 38862217
- PMCID: PMC11210254
- DOI: 10.18632/aging.205911
Disulfidptosis-related lncRNAs signature predicting prognosis and immunotherapy effect in lung adenocarcinoma
Abstract
Purpose: Lung adenocarcinoma (LUAD) is a prevalent malignant tumor worldwide, with high incidence and mortality rates. However, there is still a lack of specific and sensitive biomarkers for its early diagnosis and targeted treatment. Disulfidptosis is a newly identified mode of cell death that is characteristic of disulfide stress. Therefore, exploring the correlation between disulfidptosis-related long non-coding RNAs (DRGs-lncRNAs) and patient prognosis can provide new molecular targets for LUAD patients.
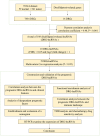
Methods: The study analysed the transcriptome data and clinical data of LUAD patients in The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) database, gene co-expression, and univariate Cox regression methods were used to screen for DRGs-lncRNAs related to prognosis. The risk score model of lncRNA was established by univariate and multivariate Cox regression models. TIMER, CIBERSORT, CIBERSORT-ABS, and other methods were used to analyze immune infiltration and further evaluate immune function analysis, immune checkpoints, and drug sensitivity. Real-time polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) was performed to detect the expression of DRGs-lncRNAs in LUAD cell lines.
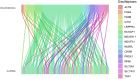
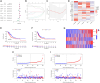
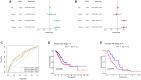
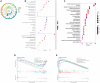
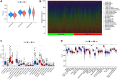
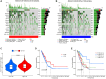
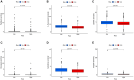
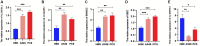
Results: A total of 108 lncRNAs significantly associated with disulfidptosis were identified. A prognostic model was constructed by screening 10 lncRNAs with independent prognostic significance through single-factor Cox regression analysis, LASSO regression analysis, and multiple-factor Cox regression analysis. Survival analysis of patients through the prognostic model showed that there were obvious survival differences between the high- and low-risk groups. The risk score of the prognostic model can be used as an independent prognostic factor independent of other clinical traits, and the risk score increases with stage. Further analysis showed that the prognostic model was also different from tumor immune cell infiltration, immune function, and immune checkpoint genes in the high- and low-risk groups. Chemotherapy drug susceptibility analysis showed that high-risk patients were more sensitive to Paclitaxel, 5-Fluorouracil, Gefitinib, Docetaxel, Cytarabine, and Cisplatin. Additionally, RT-PCR analysis demonstrated differential expression of DRGs-lncRNAs between LUAD cell lines and the human bronchial epithelial cell line.
Conclusions: The prognostic model of DRGs-lncRNAs constructed in this study has certain accuracy and reliability in predicting the survival prognosis of LUAD patients, and provides clues for the interaction between disulfidptosis and LUAD immunotherapy.
Keywords: disulfidptosis; drug sensitivity; long non-coding RNAs; lung adenocarcinoma; prognosis model.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

