Characterization of pediatric urinary microbiome at species-level resolution indicates variation due to sex, age, and urologic history
- PMID: 38862292
- PMCID: PMC11913066
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jpurol.2024.05.016
Characterization of pediatric urinary microbiome at species-level resolution indicates variation due to sex, age, and urologic history
Abstract
Background: Recently, associations between recurrent urinary tract infections (UTI) and the urinary microbiome (urobiome) composition have been identified in adults. However, little is known about the urobiome in children. We aimed to characterize the urobiome of children with species-level resolution and to identify associations based on UTI history.
Study design: Fifty-four children (31 females and 21 males) from 3 months to 11 years of age participated in the study. Catheterized urine specimens were obtained from children undergoing a clinically indicated voiding cystourethrogram. To improve the analysis of the pediatric urobiome, we used a novel protocol using filters to collect biomass from the urine coupled with synthetic long-read 16S rRNA gene sequencing to obtain culture-independent species-level resolution data. We tested for differences in microbial composition between sex and history of UTIs using non-parametric tests on individual bacteria and alpha diversity measures.
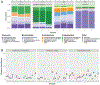
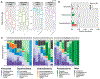
Results: We detected bacteria in 61% of samples from 54 children (mean age 40.7 months, 57% females). Similar to adults, urobiomes were distinct across individuals and varied by sex. The urobiome of females showed higher diversity as measured by the inverse Simpson and Shannon indices but not the Pielou evenness index or number of observed species (p = 0.05, p = 0.04, p = 0.35, and p = 0.11, respectively). Additionally, several species were significantly overrepresented in females compared to males, including those from the genera Anaerococcus, Prevotella, and Schaalia (p = 0.03, 0.04, and 0.02, respectively). Urobiome diversity increased with age, driven mainly by males. Comparison of children with a history of 1, 2, or 3+ UTIs revealed that urobiome diversity significantly decreases in the group that experienced 3+ UTIs as measured by the Simpson, Shannon, and Pielou indices (p = 0.03, p = 0.05, p = 0.01). Several bacteria were also found to be reduced in abundance.
Discussion: In this study, we confirm that urobiome can be identified from catheter-collected urine specimens in infants as young as 3 months, providing further evidence that the pediatric bladder is not sterile. In addition to confirming variations in the urobiome related to sex, we identify age-related changes in children under 5 years of age, which conflicts with some prior research. We additionally identify associations with a history of UTIs.
Conclusions: Our study provides additional evidence that the pediatric urobiome exists. The bacteria in the bladder of children appear to be affected by early urologic events and warrants future research.
Keywords: Pediatric urology; Urinary microbiome; Urinary tract infections; Urobiome.
Copyright © 2024 Journal of Pediatric Urology Company. Published by Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures

Update of
-
Characterization of pediatric urinary microbiome at species-level resolution indicates variation due to sex, age, and urologic history.medRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 May 17:2024.05.16.24307309. doi: 10.1101/2024.05.16.24307309. medRxiv. 2024. Update in: J Pediatr Urol. 2024 Oct;20(5):884-893. doi: 10.1016/j.jpurol.2024.05.016. PMID: 38798594 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
Comment in
-
Profiling the dynamic pediatric urobiome: Missing links and future directions!J Pediatr Urol. 2024 Oct;20(5):894-895. doi: 10.1016/j.jpurol.2024.06.029. Epub 2024 Jun 27. J Pediatr Urol. 2024. PMID: 38981782 No abstract available.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

