[Normal mouse serum alleviates radiation pneumonitis in mice by inhibiting the focal adhesion signaling pathway]
- PMID: 38862437
- PMCID: PMC11166715
- DOI: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2024.05.01
[Normal mouse serum alleviates radiation pneumonitis in mice by inhibiting the focal adhesion signaling pathway]
Abstract
Objective: To evaluate the therapeutic effect of normal mouse serum on radiation pneumonitis in mice and explore the possible mechanism.
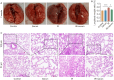
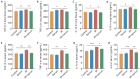
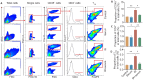
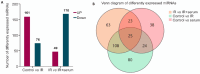
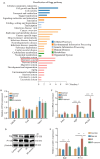
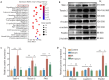
Methods: Mouse models of radiation pneumonitis induced by thoracic radiation exposure were given intravenous injections of 100 μL normal mouse serum or normal saline immediately after the exposure followed by injections once every other day for a total of 8 injections. On the 15th day after irradiation, histopathological changes of the lungs of the mice were examined using HE staining, the levels of TNF-α, TGF-β, IL-1α and IL-6 in the lung tissue and serum were detected using ELISA, and the percentages of lymphocytes in the lung tissue were analyzed with flow cytometry. High-throughput sequencing of exosome miRNA was carried out to explore the changes in the signaling pathways. The mRNA expression levels of the immune-related genes were detected by qRT-PCR, and the protein expressions of talin-1, tensin2, FAK, vinculin, α-actinin and paxillin in the focal adhesion signaling pathway were detected with Western blotting.
Results: In the mouse models of radiation pneumonitis, injections of normal mouse serum significantly decreased the lung organ coefficient, lowered the levels of TNF-α, TGF-β, IL-1α and IL-6 in the serum and lung tissues, and ameliorated infiltration of CD45+, CD4+ and Treg lymphocytes in the lung tissue (all P<0.05). The expression levels of Egfr and Pik3cd genes at both the mRNA and protein levels and the protein expressions of talin-1, tensin2, FAK, vinculin, α‑actinin and paxillin were all significantly down-regulated in the mouse models after normal mouse serum treatment.
Conclusion: Normal mouse serum ameliorates radiation pneumonitis in mice by inhibiting the expressions of key proteins in the Focal adhesion signaling pathway.
Keywords: exosomes; focal adhesion pathway; normal mouse serum; radiation pneumonitis.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
