Secretome profiling reveals acute changes in oxidative stress, brain homeostasis, and coagulation following short-duration spaceflight
- PMID: 38862464
- PMCID: PMC11166969
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-024-48841-w
Secretome profiling reveals acute changes in oxidative stress, brain homeostasis, and coagulation following short-duration spaceflight
Abstract
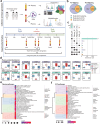
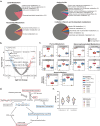
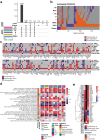
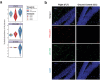
As spaceflight becomes more common with commercial crews, blood-based measures of crew health can guide both astronaut biomedicine and countermeasures. By profiling plasma proteins, metabolites, and extracellular vesicles/particles (EVPs) from the SpaceX Inspiration4 crew, we generated "spaceflight secretome profiles," which showed significant differences in coagulation, oxidative stress, and brain-enriched proteins. While >93% of differentially abundant proteins (DAPs) in vesicles and metabolites recovered within six months, the majority (73%) of plasma DAPs were still perturbed post-flight. Moreover, these proteomic alterations correlated better with peripheral blood mononuclear cells than whole blood, suggesting that immune cells contribute more DAPs than erythrocytes. Finally, to discern possible mechanisms leading to brain-enriched protein detection and blood-brain barrier (BBB) disruption, we examined protein changes in dissected brains of spaceflight mice, which showed increases in PECAM-1, a marker of BBB integrity. These data highlight how even short-duration spaceflight can disrupt human and murine physiology and identify spaceflight biomarkers that can guide countermeasure development.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
C.E.M. is a co-Founder of Cosmica Biosciences. I.M. receives research grant support/funding from Atossa Inc. A.S.G., L.W., P.T., Q.Y., J.C., R.B., A.S., and D.H. are employees of and have a financial interest in Seer Inc. and Prognomiq Inc. Jan Krumsiek holds equity in Chymia LLC and IP in PsyProtix and is cofounder of iollo. The remaining authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Martin D, Makedonas G, Crucian B, Peanlikhit T, Rithidech K. The use of the multidimensional protein identification technology (MudPIT) to analyze plasma proteome of astronauts collected before, during, and after spaceflights. Acta. Astronaut. 2022;193:9–19. doi: 10.1016/j.actaastro.2021.12.054. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

