Influence of the spaceflight environment on macrophage lineages
- PMID: 38862517
- PMCID: PMC11166655
- DOI: 10.1038/s41526-023-00293-0
Influence of the spaceflight environment on macrophage lineages
Abstract
Spaceflight and terrestrial spaceflight analogs can alter immune phenotypes. Macrophages are important immune cells that bridge the innate and adaptive immune systems and participate in immunoregulatory processes of homeostasis. Furthermore, macrophages are critically involved in initiating immunity, defending against injury and infection, and are also involved in immune resolution and wound healing. Heterogeneous populations of macrophage-type cells reside in many tissues and cause a variety of tissue-specific effects through direct or indirect interactions with other physiological systems, including the nervous and endocrine systems. It is vital to understand how macrophages respond to the unique environment of space to safeguard crew members with appropriate countermeasures for future missions in low Earth orbit and beyond. This review highlights current literature on macrophage responses to spaceflight and spaceflight analogs.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
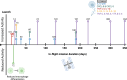
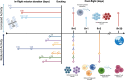
Similar articles
-
Immune System Dysregulation During Spaceflight: Potential Countermeasures for Deep Space Exploration Missions.Front Immunol. 2018 Jun 28;9:1437. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.01437. eCollection 2018. Front Immunol. 2018. PMID: 30018614 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Neuro-consequences of the spaceflight environment.Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2022 Jan;132:908-935. doi: 10.1016/j.neubiorev.2021.09.055. Epub 2021 Nov 9. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2022. PMID: 34767877 Review.
-
Terrestrial stress analogs for spaceflight associated immune system dysregulation.Brain Behav Immun. 2014 Jul;39:23-32. doi: 10.1016/j.bbi.2014.01.011. Epub 2014 Jan 24. Brain Behav Immun. 2014. PMID: 24462949 Review.
-
NK cell function is impaired during long-duration spaceflight.J Appl Physiol (1985). 2019 Apr 1;126(4):842-853. doi: 10.1152/japplphysiol.00761.2018. Epub 2018 Nov 1. J Appl Physiol (1985). 2019. PMID: 30382809
-
Changes in the Optic Nerve Head and Choroid Over 1 Year of Spaceflight.JAMA Ophthalmol. 2021 Jun 1;139(6):663-667. doi: 10.1001/jamaophthalmol.2021.0931. JAMA Ophthalmol. 2021. PMID: 33914020 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Qu-zhuo-tong-bi decoction exerts gouty arthritis therapy by skewing macrophage polarization through butanoate metabolism.Chin Med. 2025 Jul 22;20(1):115. doi: 10.1186/s13020-025-01162-6. Chin Med. 2025. PMID: 40696369 Free PMC article.
-
Wound-healing and onboard care during long-duration human deep space exploration from a surgical perspective through the lens of a scoping review.J Vasc Surg Venous Lymphat Disord. 2025 Sep;13(5):102249. doi: 10.1016/j.jvsv.2025.102249. Epub 2025 Apr 15. J Vasc Surg Venous Lymphat Disord. 2025. PMID: 40246171 Free PMC article. Review.
-
An integrative framework linking molecular signatures and locomotory phenotypes in space-induced sarcopenia.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2025 May 8:2025.05.03.652040. doi: 10.1101/2025.05.03.652040. bioRxiv. 2025. PMID: 40654681 Free PMC article. Preprint.
-
A second space age spanning omics, platforms and medicine across orbits.Nature. 2024 Aug;632(8027):995-1008. doi: 10.1038/s41586-024-07586-8. Epub 2024 Jun 11. Nature. 2024. PMID: 38862027 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Simulated Microgravity Alters Gene Regulation Linked to Immunity and Cardiovascular Disease.Genes (Basel). 2024 Jul 24;15(8):975. doi: 10.3390/genes15080975. Genes (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39202335 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

