Space radiation damage rescued by inhibition of key spaceflight associated miRNAs
- PMID: 38862542
- PMCID: PMC11166944
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-024-48920-y
Space radiation damage rescued by inhibition of key spaceflight associated miRNAs
Abstract
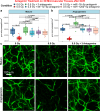
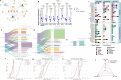
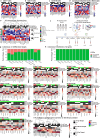
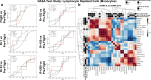
Our previous research revealed a key microRNA signature that is associated with spaceflight that can be used as a biomarker and to develop countermeasure treatments to mitigate the damage caused by space radiation. Here, we expand on this work to determine the biological factors rescued by the countermeasure treatment. We performed RNA-sequencing and transcriptomic analysis on 3D microvessel cell cultures exposed to simulated deep space radiation (0.5 Gy of Galactic Cosmic Radiation) with and without the antagonists to three microRNAs: miR-16-5p, miR-125b-5p, and let-7a-5p (i.e., antagomirs). Significant reduction of inflammation and DNA double strand breaks (DSBs) activity and rescue of mitochondria functions are observed after antagomir treatment. Using data from astronaut participants in the NASA Twin Study, Inspiration4, and JAXA missions, we reveal the genes and pathways implicated in the action of these antagomirs are altered in humans. Our findings indicate a countermeasure strategy that can potentially be utilized by astronauts in spaceflight missions to mitigate space radiation damage.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Circulating miRNA Spaceflight Signature Reveals Targets for Countermeasure Development.Cell Rep. 2020 Dec 8;33(10):108448. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2020.108448. Epub 2020 Nov 25. Cell Rep. 2020. PMID: 33242410 Free PMC article.
-
NASA study of cataract in astronauts (NASCA). Report 1: Cross-sectional study of the relationship of exposure to space radiation and risk of lens opacity.Radiat Res. 2009 Jul;172(1):10-20. doi: 10.1667/RR1580.1. Radiat Res. 2009. PMID: 19580503
-
Radiation-induced ophthalmic risks of long duration spaceflight: Current investigations and interventions.Eur J Ophthalmol. 2024 Sep;34(5):1337-1345. doi: 10.1177/11206721231221584. Epub 2023 Dec 27. Eur J Ophthalmol. 2024. PMID: 38151034 Review.
-
Temporal Telomere and DNA Damage Responses in the Space Radiation Environment.Cell Rep. 2020 Dec 8;33(10):108435. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2020.108435. Epub 2020 Nov 25. Cell Rep. 2020. PMID: 33242411
-
Getting ready for the manned mission to Mars: the astronauts' risk from space radiation.Naturwissenschaften. 2007 Jul;94(7):517-26. doi: 10.1007/s00114-006-0204-0. Epub 2007 Jan 19. Naturwissenschaften. 2007. PMID: 17235598 Review.
Cited by
-
An Update on Neuroaging on Earth and in Spaceflight.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Feb 18;26(4):1738. doi: 10.3390/ijms26041738. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40004201 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Presymptomatic microRNA-based biomarker signatures for the prognosis of localized radiation injury in mice.PLoS One. 2025 Aug 8;20(8):e0329737. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0329737. eCollection 2025. PLoS One. 2025. PMID: 40779592 Free PMC article.
-
miRTarBase 2025: updates to the collection of experimentally validated microRNA-target interactions.Nucleic Acids Res. 2025 Jan 6;53(D1):D147-D156. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkae1072. Nucleic Acids Res. 2025. PMID: 39578692 Free PMC article.
-
A second space age spanning omics, platforms and medicine across orbits.Nature. 2024 Aug;632(8027):995-1008. doi: 10.1038/s41586-024-07586-8. Epub 2024 Jun 11. Nature. 2024. PMID: 38862027 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Taking the 3Rs to a higher level: replacement and reduction of animal testing in life sciences in space research.Biotechnol Adv. 2025 Jul-Aug;81:108574. doi: 10.1016/j.biotechadv.2025.108574. Epub 2025 Apr 1. Biotechnol Adv. 2025. PMID: 40180136 Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

