Associations of lifestyle characteristics with circulating immune markers in the general population based on NHANES 1999 to 2014
- PMID: 38862546
- PMCID: PMC11166635
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-024-63875-2
Associations of lifestyle characteristics with circulating immune markers in the general population based on NHANES 1999 to 2014
Abstract
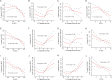
Lifestyles maybe associated with the immune and inflammatory state of human body. We aimed to comprehensively explore the relationship between lifestyles and circulating immune-inflammatory markers in the general population. Data from NHANES 1999-2014 was used. Lifestyle factors included leisure-time physical activity (LTPA), diet quality (Healthy Eating Index-2015, HEI-2015), alcohol consumption, cigarettes smoking, sleep hour and sedentary time. Immune makers included C-reactive protein (CRP), neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio (NLR), systemic immune-inflammation index (SII), platelet-lymphocyte ratio (PLR) and monocyte-lymphocyte ratio (MLR). Generalized linear regression models were used to adjust confounders. Regressions of restricted cubic splines were utilized to evaluate the potentially non-linear relationships between exposures and outcomes. As results, HEI was negatively associated with CRP (P < 0.001), SII (P < 0.001), and NLR (P < 0.001). Cigarettes per day was positively associated with CRP (P < 0.001), SII (P < 0.001), and NLR (P = 0.008). Alcohol consumption was negatively associated with CRP (P < 0.001), but positively associated with PLR (P = 0.012) and MLR (P < 0.001). Physical activity was negatively associated with CRP (P < 0.001), SII (P = 0.005), and NLR (P = 0.002), but positively associated with PLR (P = 0.010). Participants with higher healthy lifestyle score had significantly lower CRP, SII and NLR (all P values < 0.05). Most of the sensitivity analyses found similar results. In conclusion, we found significant associations between lifestyles and immune markers in the general population, which may reflect a systemic inflammatory response to unhealthy lifestyles.
Keywords: Alcohol consumption; Cigarettes smoking; Diet quality; Immune-inflammatory markers; Leisure-time physical activity; NHANES.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Evaluation of the inflammatory parameters as potential biomarkers of systemic inflammation extent and the disease severity in psoriasis patients.Arch Dermatol Res. 2024 May 24;316(6):229. doi: 10.1007/s00403-024-02972-8. Arch Dermatol Res. 2024. PMID: 38787405
-
The relationship between a series of inflammatory markers on the risk of heart failure in different gender groups: Analysis from NHANES 2015-2018.PLoS One. 2024 Mar 25;19(3):e0296936. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0296936. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 38527048 Free PMC article.
-
Association between systemic inflammatory indicators with the survival of chronic kidney disease: a prospective study based on NHANES.Front Immunol. 2024 Apr 8;15:1365591. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1365591. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38650947 Free PMC article.
-
Inflammatory markers are associated with infertility prevalence: a cross-sectional analysis of the NHANES 2013-2020.BMC Public Health. 2024 Jan 18;24(1):221. doi: 10.1186/s12889-024-17699-4. BMC Public Health. 2024. PMID: 38238731 Free PMC article.
-
[The role of immuno-inflammatory factors in the development of negative symptoms in schizophrenia].Zh Nevrol Psikhiatr Im S S Korsakova. 2024;124(11):42-48. doi: 10.17116/jnevro202412411142. Zh Nevrol Psikhiatr Im S S Korsakova. 2024. PMID: 39690550 Review. Russian.
Cited by
-
Genetically Predicted Leucine Level Mediates Association Between CD4/CD8br T Lymphocytes and Insomnia.Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2025 Jan 22;45(1):15. doi: 10.1007/s10571-025-01533-5. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2025. PMID: 39841266 Free PMC article.
-
Systemic immune-inflammatory index mediates the association between regular walking and depression in the elderly with coronary heart disease.BMC Geriatr. 2025 Jun 6;25(1):414. doi: 10.1186/s12877-025-06085-3. BMC Geriatr. 2025. PMID: 40481425 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of alcohol consumption on outcomes and potential of immune biomarkers for postoperative complications in trauma patients.Front Immunol. 2025 Apr 14;16:1492288. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1492288. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40297586 Free PMC article.
-
Association between United States Environmental Contaminants and the Prevalence of Psoriasis Derived from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey.Toxics. 2024 Jul 19;12(7):522. doi: 10.3390/toxics12070522. Toxics. 2024. PMID: 39058174 Free PMC article.
-
Saturation effects of the relationship between physical exercise and systemic immune inflammation index in the short-sleep population: a cross-sectional study.BMC Public Health. 2024 Jul 17;24(1):1920. doi: 10.1186/s12889-024-19432-7. BMC Public Health. 2024. PMID: 39020383 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Gupta K, Kalra R, Pate M, Nagalli S, Ather S, Rajapreyar I, et al. Relative predictive value of circulating immune markers in US adults without cardiovascular disease: Implications for risk reclassification. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2021;96(7):1812–1821. doi: 10.1016/j.mayocp.2020.11.027. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

