Survival of patients with ruptured gastrointestinal stromal tumour treated with adjuvant imatinib in a randomised trial
- PMID: 38862742
- PMCID: PMC11263706
- DOI: 10.1038/s41416-024-02738-z
Survival of patients with ruptured gastrointestinal stromal tumour treated with adjuvant imatinib in a randomised trial
Abstract
Background: Patients with ruptured gastrointestinal stromal tumour (GIST) have poor prognosis. Little information is available about how adjuvant imatinib influences survival.
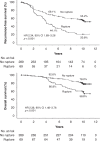
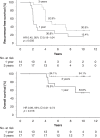
Methods: We explored recurrence-free survival (RFS) and overall survival (OS) of patients with ruptured GIST who participated in a randomised trial (SSG XVIII/AIO), where 400 patients with high-risk GIST were allocated to adjuvant imatinib for either 1 year or 3 years after surgery. Of the 358 patients with confirmed localised GIST, 73 (20%) had rupture reported. The ruptures were classified retrospectively using the Oslo criteria.
Results: Most ruptures were major, four reported ruptures were reclassified unruptured. The 69 patients with rupture had inferior RFS and OS compared with 289 patients with unruptured GIST (10-year RFS 21% vs. 55%, OS 59% vs. 78%, respectively). Three-year adjuvant imatinib did not significantly improve RFS or OS of the patients with rupture compared with 1-year treatment, but in the largest mutational subset with KIT exon 11 deletion/indel mutation OS was higher in the 3-year group than in the 1-year group (10-year OS 94% vs. 54%).
Conclusions: About one-fifth of ruptured GISTs treated with adjuvant imatinib did not recur during the first decade of follow-up. Relatively high OS rates were achieved despite rupture.
Clinical trial registration: NCT00116935.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
HJ has a consulting/advisory role in Orion Pharma, Neutron Therapeutics, and Maud Kuistila Foundation, has received research grants from Mersana Therapeutics and Defence Therapeutics, and has stock ownership in Orion Pharma and Sartar Therapeutics. ME has received consulting fees from Blueprint Medicines and institutional research funding from Novartis. PH has received honoraria and research support from Novartis. KB has had a consulting or advisory roles for Bayer, GSK, Incyte, Deciphera, and NEC Oncoimmunity; invited speaker roles for Lilly, Novartis, and Deciphera Pharmaceuticals, LLC; and institutional research funding from Lilly and Merck. PJJ has had a consulting or advisory role, received honoraria, research funding, and/or travel/accommodation expenses from Bayer, Boehringer, Novartis, Pfizer, Servier, Roche, BMS and Celgene, Pierre Fabre, Janssen/Johnson&Johnson, MSD, Merck, and AstraZeneca. SB has received institutional research funding from Blueprint Medicines, Incyte, and Novartis, honoraria from PharmaMar, Eli Lilly & Co, and Novartis, has an advisory role in Adcendo, Bayer, Blueprint Medicines, Böhringer Ingelheim, Daiichi Sankyo, Deciphera, Eli Lilly & Co, GSK, Exelixis, Nanobiotix, Novartis, and Roche, and has received travel support from PharmaMar. PMJ has received honoraria from Ipsen, MSD, and Orion Pharma. EW has received honoraria from Bayer, Novartis, Roche, Bristol Myers Squibb, and Boehringer Ingelheim. PR has received honoraria for participation in Advisory Boards for Bayer, Novartis, Roche, Deciphera, Mundibiopharma, PharmaMar, Blueprint Medicines, GSK, Boehringer Ingelheim and for lectures for Deciphera, PharmaMar, and Boehringer Ingelheim. The remaining authors declare no potential conflicts.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Effect of KIT and PDGFRA Mutations on Survival in Patients With Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumors Treated With Adjuvant Imatinib: An Exploratory Analysis of a Randomized Clinical Trial.JAMA Oncol. 2017 May 1;3(5):602-609. doi: 10.1001/jamaoncol.2016.5751. JAMA Oncol. 2017. PMID: 28334365 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Survival Outcomes Associated With 3 Years vs 1 Year of Adjuvant Imatinib for Patients With High-Risk Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumors: An Analysis of a Randomized Clinical Trial After 10-Year Follow-up.JAMA Oncol. 2020 Aug 1;6(8):1241-1246. doi: 10.1001/jamaoncol.2020.2091. JAMA Oncol. 2020. PMID: 32469385 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
KIT and PDGFRA Mutations and Survival of Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumor Patients Treated with Adjuvant Imatinib in a Randomized Trial.Clin Cancer Res. 2023 Sep 1;29(17):3313-3319. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-22-3980. Clin Cancer Res. 2023. PMID: 37014660 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Adjuvant treatment of gastrointestinal stromal tumor: State of the art in 2025.Eur J Cancer. 2025 Jun 3;222:115473. doi: 10.1016/j.ejca.2025.115473. Epub 2025 Apr 26. Eur J Cancer. 2025. PMID: 40306119 Review.
-
Deciding on the duration of adjuvant therapy in gastrointestinal stromal tumor.Expert Rev Anticancer Ther. 2021 May;21(5):547-556. doi: 10.1080/14737140.2021.1863149. Epub 2020 Dec 23. Expert Rev Anticancer Ther. 2021. PMID: 33353442 Review.
Cited by
-
Minimally invasive approaches to small gastric stromal tumors: The less with the more.World J Gastrointest Surg. 2025 May 27;17(5):101823. doi: 10.4240/wjgs.v17.i5.101823. World J Gastrointest Surg. 2025. PMID: 40502497 Free PMC article.
-
What kind of tumour rupture requires adjuvant therapy?Br J Cancer. 2024 Oct;131(7):1109-1110. doi: 10.1038/s41416-024-02812-6. Epub 2024 Aug 27. Br J Cancer. 2024. PMID: 39191892 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Spontaneous Terminal Ileum GIST Perforation Causing an Acute Abdomen in an Elderly Patient-A Rare Case.Diagnostics (Basel). 2025 Jul 18;15(14):1816. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics15141816. Diagnostics (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40722565 Free PMC article.
References
-
- de Pinieux G, Karanian M, Le Loarer F, Le Guellec S, Chabaud S, Terrier P, et al. Nationwide incidence of sarcomas and connective tissue tumors of intermediate malignancy over four years using an expert pathology review network. PLoS One. 2021;16:e0246958. 10.1371/journal.pone.0246958 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Hølmebakk T, Hompland I, Bjerkehagen B, Stoldt S, Bruland ØS, Sundby Hall K, et al. Recurrence-free survival after resection of gastric gastrointestinal stromal tumors classified according to a strict definition of tumor rupture: a population-based study. Ann Surg Oncol. 2018;25:1133–9. 10.1245/s10434-018-6353-5 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

