THBru attenuates diabetic cardiomyopathy by inhibiting RAGE-dependent inflammation
- PMID: 38862818
- PMCID: PMC11420355
- DOI: 10.1038/s41401-024-01307-7
THBru attenuates diabetic cardiomyopathy by inhibiting RAGE-dependent inflammation
Erratum in
-
Author Correction: THBru attenuates diabetic cardiomyopathy by inhibiting RAGE-dependent inflammation.Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2025 Jun;46(6):1795-1796. doi: 10.1038/s41401-025-01483-0. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2025. PMID: 39885313 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
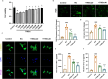
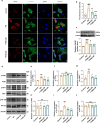
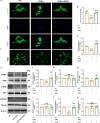
Diabetic cardiomyopathy (DCM) is a complication of diabetes mellitus characterized by heart failure and cardiac remodeling. Previous studies show that tetrahydroberberrubine (THBru) retrogrades cardiac aging by promoting PHB2-mediated mitochondrial autophagy and prevents peritoneal adhesion by suppressing inflammation. In this study we investigated whether THBru exerted protective effect against DCM in db/db mice and potential mechanisms. Eight-week-old male db/db mice were administered THBru (25, 50 mg·kg-1·d-1, i.g.) for 12 weeks. Cardiac function was assessed using echocardiography. We showed that THBru administration significantly improved both cardiac systolic and diastolic function, as well as attenuated cardiac remodeling in db/db mice. In primary neonatal mouse cardiomyocytes (NMCMs), THBru (20, 40 μM) dose-dependently ameliorated high glucose (HG)-induced cell damage, hypertrophy, inflammatory cytokines release, and reactive oxygen species (ROS) production. Using Autodock, surface plasmon resonance (SPR) and DARTS analyses, we revealed that THBru bound to the domain of the receptor for advanced glycosylation end products (RAGE), subsequently leading to inactivation of the PI3K/AKT/NF-κB pathway. Importantly, overexpression of RAGE in NMCMs reversed HG-induced inactivation of the PI3K/AKT/NF-κB pathway and subsequently counteracted the beneficial effects mediated by THBru. We conclude that THBru acts as an inhibitor of RAGE, leading to inactivation of the PI3K/AKT/NF-κB pathway. This action effectively alleviates the inflammatory responses and oxidative stress in cardiomyocytes, ultimately leading to ameliorated DCM.
Keywords: RAGE; diabetic cardiomyopathy; inflammation; tetrahydroberberrubine.
© 2024. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Shanghai Institute of Materia Medica, Chinese Academy of Sciences and Chinese Pharmacological Society.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



References
-
- Li H, Yang Q, Huang Z, Liang C, Zhang DH, Shi HT, et al. Dual-specificity phosphatase 12 attenuates oxidative stress injury and apoptosis in diabetic cardiomyopathy via the ASK1-JNK/p38 signaling pathway. Free Radic Biol Med. 2022;192:13–24. - PubMed
-
- Liu Y, Zhang H, Dai X, Zhu R, Chen B, Xia B, et al. A comprehensive review on the phytochemistry, pharmacokinetics, and antidiabetic effect of Ginseng. Phytomedicine. 2021;92:153717. - PubMed
-
- Ali T, Rahman S, Hao Q, Li W, Liu Z, Ali Shah F, et al. Melatonin prevents neuroinflammation and relieves depression by attenuating autophagy impairment through FOXO3a regulation. J Pineal Res. 2020;69:e12667. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

