Determinants of and interventions for Proton Pump Inhibitor prescription behavior: A systematic scoping review
- PMID: 38862886
- PMCID: PMC11165893
- DOI: 10.1186/s12875-024-02459-5
Determinants of and interventions for Proton Pump Inhibitor prescription behavior: A systematic scoping review
Abstract
Background: Proton Pump Inhibitors (PPI) are frequently prescribed. Long-term use is associated with side-effects and patients often lack a valid indication. Inappropriate PPI prescribing thus needs to be addressed. This review aims to scope 1) what determinants are studied as reasons for PPI prescribing, 2) what strategies are used for changing PPI (de)prescribing, and 3) whether important determinants are addressed in these interventions.
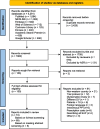
Methods: We searched eight databases for papers on determinants of physician PPI prescribing. Studies were included if they were conducted in a Western country and focused on oral PPIs for an adult population. By following the Behaviour Change Wheel, we extracted information regarding PPI prescribing behavior, behavioral determinants and intervention strategies.
Findings: We included 74 papers. Most focused on the determinants knowledge and beliefs about consequences. The latter was consistently related to PPI prescribing. Results for knowledge were mixed. Most interventions used education or enablement (e.g., algorithms, quality check improvements, involvement of pharmacists) as strategies. Enablement consistently improved PPI prescribing, while results for education were mixed.
Interpretation: There is an overemphasis on reflective processes in studies on PPI prescribing. Future research should comprehensively identify behavioral determinants, focusing on reflective and impulsive processes, such that interventions can address the most important determinants.
Keywords: Behavioral determinants; Behaviour Change Wheel; Prescribing behavior; Proton pump inhibitors.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Similar articles
-
Changes in proton pump inhibitor prescribing trend over the past decade and pharmacists' effect on prescribing practice at a tertiary hospital.BMC Health Serv Res. 2018 Jul 11;18(1):537. doi: 10.1186/s12913-018-3358-5. BMC Health Serv Res. 2018. PMID: 29996830 Free PMC article.
-
[Impact of an evaluation of the professional practices on the relevance of proton pump inhibitors prescriptions pertinence at the hospital].Rev Med Interne. 2018 Aug;39(8):618-626. doi: 10.1016/j.revmed.2018.03.006. Epub 2018 Apr 5. Rev Med Interne. 2018. PMID: 29628172 French.
-
Prescribing of proton pump inhibitors for gastrointestinal bleeding prophylaxis in the Lebanese outpatient setting: patterns, compliance with guidelines and risks.Int J Pharm Pract. 2019 Aug;27(4):386-392. doi: 10.1111/ijpp.12537. Epub 2019 Apr 3. Int J Pharm Pract. 2019. PMID: 30942513
-
Is there a role for proton pump inhibitor prophylaxis in haematology patients?Intern Med J. 2019 Jun;49(6):694-701. doi: 10.1111/imj.14241. Intern Med J. 2019. PMID: 30719802 Review.
-
AGA Clinical Practice Update on De-Prescribing of Proton Pump Inhibitors: Expert Review.Gastroenterology. 2022 Apr;162(4):1334-1342. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2021.12.247. Epub 2022 Feb 17. Gastroenterology. 2022. PMID: 35183361 Review.
References
-
- Stichting Farmaceutische Kengetallen. Data en feiten 2023. Het jaar 2022 in cijfers. 2023. Cited 2023 Sep 15. Available from: https://www.sfk.nl/publicaties/data-en-feiten/data-en-feiten-2023/view.
-
- De Jongh E, De Wit N, Numans M, Smeink P, Van der Weele G, Wesseler G. NHG-Standaard Maagklachten (M36). 2021. Available from: https://richtlijnen.nhg.org/standaarden/maagklachten.
-
- van Marrewijk CJ, Mujakovic S, Fransen GAJ, Numans ME, de Wit NJ, Muris JWM. Effect and cost-effectiveness of step-up versus step-down treatment with antacids, H2-receptor antagonists, and proton pump inhibitors in patients with new onset dyspepsia (DIAMOND study): a primary-care-based randomised controlled trial. 2009;373:215–25. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources