Impact of neuromuscular block on myocardial injury after non-cardiac surgery (MINS) incidence in the early postoperative stage of older patients undergoing laparoscopic colorectal cancer resection: a randomized controlled study
- PMID: 38862916
- PMCID: PMC11167868
- DOI: 10.1186/s12877-024-05125-8
Impact of neuromuscular block on myocardial injury after non-cardiac surgery (MINS) incidence in the early postoperative stage of older patients undergoing laparoscopic colorectal cancer resection: a randomized controlled study
Abstract
Background: Myocardial injury after non-cardiac surgery (MINS) is a common and serious complication in older patients. This study investigates the impact of neuromuscular block on the MINS incidence and other cardiovascular complications in the early postoperative stage of older patients undergoing laparoscopic colorectal cancer resection.
Methods: 70 older patients who underwent laparoscopic colorectal cancer resection were separated into the deep neuromuscular block group and moderate neuromuscular block group for 35 cases in each group (n = 1:1). The deep neuromuscular block group maintained train of four (TOF) = 0, post-tetanic count (PTC) 1-2, and the moderate neuromuscular block group maintained TOF = 1-2 during the operation. Sugammadex sodium was used at 2 mg/kg or 4 mg/kg for muscle relaxation antagonism at the end of surgery. The MINS incidence was the primary outcome and compared with Fisher's exact test. About the secondary outcomes, the postoperative pain was analyzed with Man-Whitney U test, the postoperative nausea and vomiting (PONV) and the incidence of cardiovascular complications were analyzed with Chi-square test, intraoperative mean artery pressure (MAP) and cardiac output (CO) ratio to baseline, length of stay and dosage of anesthetics were compared by two independent samples t-test.
Results: MINS was not observed in both groups. The highest incidence of postoperative cardiovascular complications was lower limbs deep vein thrombosis (14.3% in deep neuromuscular block group and 8.6% in moderate neuromuscular group). The numeric rating scale (NRS) score in the deep neuromuscular block group was lower than the moderate neuromuscular block group 72 h after surgery (0(1,2) vs 0(1,2), P = 0.018). The operation time in the deep neuromuscular block group was longer (356.7(107.6) vs 294.8 (80.0), min, P = 0.008), the dosage of propofol and remifentanil was less (3.4 (0.7) vs 3.8 (1.0), mg·kg-1·h-1, P = 0.043; 0.2 (0.06) vs 0.3 (0.07), μg·kg-1·min-1, P < 0.001), and the length of hospital stay was shorter than the moderate neuromuscular block group (18.4 (4.9) vs 22.0 (8.3), day, P = 0.028). The differences of other outcomes were not statistically significant.
Conclusions: Maintaining different degrees of the neuromuscular block under TOF guidance did not change the MINS incidence within 7 days after surgery in older patients who underwent laparoscopic colorectal cancer resection.
Trial registration: The present study was registered in the Chinese Clinical Trial Registry (10/02/2021, ChiCTR2100043323).
Keywords: Deep neuromuscular block; MINS; Moderate neuromuscular block; Older patients; Sugammadex sodium.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
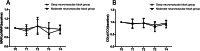
Similar articles
-
Effect of Deep Versus Moderate Neuromuscular Block on Pain After Laparoscopic Colorectal Surgery: A Randomized Clinical Trial.Dis Colon Rectum. 2021 Apr 1;64(4):475-483. doi: 10.1097/DCR.0000000000001854. Dis Colon Rectum. 2021. PMID: 33651007 Clinical Trial.
-
[The effect of deep neuromuscular block combined with low pneumoperitoneum pressure on postoperative pain in patients undergoing laparoscopic radical colorectal surgery].Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2024 Apr 2;104(13):1057-1063. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn112137-20231011-00704. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2024. PMID: 38561301 Clinical Trial. Chinese.
-
Impact of deep neuromuscular blockade on intraoperative NOL-guided remifentanil requirement during desflurane anesthesia in laparoscopic colorectal surgeries: A randomised controlled trial.J Clin Anesth. 2024 Dec;99:111659. doi: 10.1016/j.jclinane.2024.111659. Epub 2024 Oct 23. J Clin Anesth. 2024. PMID: 39447530 Clinical Trial.
-
Laparoscopic surgery and muscle relaxants: is deep block helpful?Anesth Analg. 2015 Jan;120(1):51-58. doi: 10.1213/ANE.0000000000000471. Anesth Analg. 2015. PMID: 25625254 Review.
-
Sugammadex, the Guardian of Deep Muscle Relaxation During Conventional and Robot-Assisted Laparoscopic Surgery: A Narrative Review.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2021 Sep 14;15:3893-3901. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S328682. eCollection 2021. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2021. PMID: 34548781 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Botto F, Alonso-Coello P, Chan MT, et al. Myocardial injury after noncardiac surgery: a large, international, prospective cohort study establishing diagnostic criteria, characteristics, predictors, and 30-day outcomes. Anesthesiology. 2014;120:564–578. doi: 10.1097/ALN.0000000000000113. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

