Global, regional and national burdens of Nasopharynx cancer in the adolescents and young adults from 1990 to 2019 and its predictions
- PMID: 38862937
- PMCID: PMC11167860
- DOI: 10.1186/s12885-024-12480-7
Global, regional and national burdens of Nasopharynx cancer in the adolescents and young adults from 1990 to 2019 and its predictions
Abstract
Purpose: To use data from the Global Burden of Disease (GBD) Study 2019 to report the global, regional and national rates and trends of deaths incidence, prevalence, disability-adjusted life years (DALYs) for Nasopharynx cancer (NPC) in adolescents and young adults (AYAs).
Methods: Data from the GBD 2019 were used to analyze deaths incidence, prevalence and DALYs due to NPC at global, regional, and national levels. Joinpoint regression analysis was used to calculate the average annual percentage changes (AAPC). The association between incidence, prevalence and DALYs and socioeconomic development was analyzed using the GBD Socio-demographic Index (SDI). Finally, projections were made until 2030 and calculated in Nordpred.
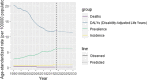
Results: The incidence, prevalence, death and DALYs rates (95%UI) due to NPC 0.96 (0.85-1.09, 6.31 (5.54-7.20),0.20 (0.19-0.22), and 12.23(11.27-13.29) in 2019, respectively. From 1990 to 2019, the incidence and prevalence rates increased by 1.79 (95% CI 1.03 to 2.55) and 2.97(95% CI 2.13 to 3.82) respectively while the deaths and DALYs rates declined by 1.64(95%CI 1.78 to 1.49) and 1.6(95%CI 1.75 to 1.4) respectively. Deaths and DALYs rates in South Asia, East Asia, North Africa and Middle East decreased with SDI. Incidence and prevalence rates in East Asia increased with SDI. At the national level, the incidence and prevalence rates are high in China, Taiwan(China), Singapore, Malaysia, Brunel Darussalam, Algeria, Tunisia, Libya and Malta. Meanwhile, the deaths and DALYs rates are still high in Malaysia, Brunel Darussalam, Greenland and Taiwan(Province of China). The deaths and DALYs rates are low in Honduras, Finland and Norway. From the 2020 to 2030, ASIR、ASPR and ASDR in most regions are predicted to stable, but DALYs tends to decline.
Conclusion: NPC in AYAs is a significant global public problem. The incidence, prevalence, and DALYs rates vary widely by region and country. Therefore different regions and countries should be targeted to improve the disease burden of NPC.
Keywords: Adolescents and young adults; Disease burden; Nasopharynx cancer; Prediction.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




Similar articles
-
The burden of low back pain in adolescents and young adults.J Back Musculoskelet Rehabil. 2024;37(4):955-966. doi: 10.3233/BMR-230215. J Back Musculoskelet Rehabil. 2024. PMID: 38517768 Free PMC article.
-
Global burden of subarachnoid hemorrhage among adolescents and young adults aged 15-39 years: A trend analysis study from 1990 to 2021.PLoS One. 2024 Dec 20;19(12):e0316111. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0316111. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 39705242 Free PMC article.
-
Global, regional, and national burdens of rheumatoid arthritis among people aged 60 years and older from 1990 to 2021: a trend analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2021.Front Public Health. 2025 May 26;13:1527680. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2025.1527680. eCollection 2025. Front Public Health. 2025. PMID: 40491992 Free PMC article.
-
Global, regional, and national epidemiology of nasopharyngeal carcinoma in middle-aged and elderly patients from 1990 to 2021.Ageing Res Rev. 2025 Feb;104:102613. doi: 10.1016/j.arr.2024.102613. Epub 2024 Dec 1. Ageing Res Rev. 2025. PMID: 39626854 Review.
-
Global, regional, and national burden of 12 mental disorders in 204 countries and territories, 1990-2019: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019.Lancet Psychiatry. 2022 Feb;9(2):137-150. doi: 10.1016/S2215-0366(21)00395-3. Epub 2022 Jan 10. Lancet Psychiatry. 2022. PMID: 35026139 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Global, regional and national burden of pancreatic cancer and its attributable risk factors from 2019 to 2021, with projection to 2044.Front Oncol. 2025 Jan 14;14:1521788. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2024.1521788. eCollection 2024. Front Oncol. 2025. PMID: 39876895 Free PMC article.
-
Global and regional burden of nasopharyngeal cancer in older adults attributable to smoking and high alcohol use from 1990 to 2021.Front Public Health. 2025 Jun 12;13:1614389. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2025.1614389. eCollection 2025. Front Public Health. 2025. PMID: 40575097 Free PMC article.
-
A bibliometric analysis of nasopharyngeal carcinoma radiomics: trends and insights.Front Oncol. 2025 Mar 25;15:1506778. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2025.1506778. eCollection 2025. Front Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40201350 Free PMC article.
-
Global, regional, and national burdens of alcohol-related cirrhosis among women from 1992 to 2021 and its predictions.Sci Rep. 2025 Mar 31;15(1):10959. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-95563-0. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40164772 Free PMC article.
-
Global, regional, and national burden and trends of HIV/AIDS among women of childbearing age from 1990 to 2021: results from Global Burden of Disease 2021.Front Med (Lausanne). 2025 Jul 4;12:1605092. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2025.1605092. eCollection 2025. Front Med (Lausanne). 2025. PMID: 40687711 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Vollset SE, et al. Fertility, mortality, migration, and population scenarios for 195 countries and territories from 2017 to 2100: a forecasting analysis for the global burden of disease study. Lancet (London, England) 2020;396(10258):1285–1306. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30677-2. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Global age-sex-specific fertility mortality, healthy life expectancy (HALE), and population estimates in 204 countries and territories, 1950–2019: a comprehensive demographic analysis for the global burden of disease study 2019. Lancet (London, England) 2020;396(10258):1160–1203. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30977-6. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

