Motor skill learning modulates striatal extracellular vesicles' content in a mouse model of Huntington's disease
- PMID: 38863004
- PMCID: PMC11167907
- DOI: 10.1186/s12964-024-01693-9
Motor skill learning modulates striatal extracellular vesicles' content in a mouse model of Huntington's disease
Abstract
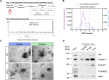
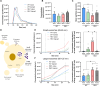
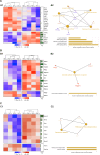
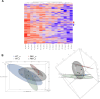
Huntington's disease (HD) is a neurological disorder caused by a CAG expansion in the Huntingtin gene (HTT). HD pathology mostly affects striatal medium-sized spiny neurons and results in an altered cortico-striatal function. Recent studies report that motor skill learning, and cortico-striatal stimulation attenuate the neuropathology in HD, resulting in an amelioration of some motor and cognitive functions. During physical training, extracellular vesicles (EVs) are released in many tissues, including the brain, as a potential means for inter-tissue communication. To investigate how motor skill learning, involving acute physical training, modulates EVs crosstalk between cells in the striatum, we trained wild-type (WT) and R6/1 mice, the latter with motor and cognitive deficits, on the accelerating rotarod test, and we isolated their striatal EVs. EVs from R6/1 mice presented alterations in the small exosome population when compared to WT. Proteomic analyses revealed that striatal R6/1 EVs recapitulated signaling and energy deficiencies present in HD. Motor skill learning in R6/1 mice restored the amount of EVs and their protein content in comparison to naïve R6/1 mice. Furthermore, motor skill learning modulated crucial pathways in metabolism and neurodegeneration. All these data provide new insights into the pathogenesis of HD and put striatal EVs in the spotlight to understand the signaling and metabolic alterations in neurodegenerative diseases. Moreover, our results suggest that motor learning is a crucial modulator of cell-to-cell communication in the striatum.
Keywords: Cortico-striatal activation; Extracellular vesicles; Huntington’s disease; Motor learning; Proteomics; Striatum.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Cerulenin partially corrects the disrupted developmental transcriptomic signature in Huntington's disease striatal medium spiny neurons.Stem Cells. 2025 Jul 21;43(8):sxaf029. doi: 10.1093/stmcls/sxaf029. Stem Cells. 2025. PMID: 40336225 Free PMC article.
-
Structural and functional features of medium spiny neurons in the BACHDΔN17 mouse model of Huntington's Disease.PLoS One. 2020 Jun 23;15(6):e0234394. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0234394. eCollection 2020. PLoS One. 2020. PMID: 32574176 Free PMC article.
-
Absence of hippocampal pathology persists in the Q175DN mouse model of Huntington's disease despite elevated HTT aggregation.J Huntingtons Dis. 2025 Feb;14(1):59-84. doi: 10.1177/18796397251316762. Epub 2025 Feb 3. J Huntingtons Dis. 2025. PMID: 39973391 Free PMC article.
-
Brain incoming call from glia during neuroinflammation: Roles of extracellular vesicles.Neurobiol Dis. 2024 Oct 15;201:106663. doi: 10.1016/j.nbd.2024.106663. Epub 2024 Sep 7. Neurobiol Dis. 2024. PMID: 39251030 Review.
-
Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Extracellular Vesicles: Emerging Therapies for Neurodegenerative Diseases.Int J Nanomedicine. 2025 Jul 2;20:8547-8565. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S526945. eCollection 2025. Int J Nanomedicine. 2025. PMID: 40620684 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Small Extracellular Vesicles in Neurodegenerative Disease: Emerging Roles in Pathogenesis, Biomarker Discovery, and Therapy.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Jul 26;26(15):7246. doi: 10.3390/ijms26157246. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40806377 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- #FPU18/00194/Ministerio de Ciencia e Innovación
- FPU21/02928/Ministerio de Ciencia e Innovación
- PID2020-119236RB-I00/Ministerio de Ciencia e Innovación
- PID2019-106447RB-I00/Ministerio de Ciencia e Innovación
- PID2021-124896OA-I000/Ministerio de Ciencia e Innovación
- PID2020-119386RB-I00/Ministerio de Ciencia e Innovación
- SAF2017-88812-R/Ministerio de Ciencia e Innovación
- FI-B-00378/Agència de Gestió d'Ajuts Universitaris i de Recerca
- MJFF-000858/Michael J. Fox Foundation for Parkinson's Research
- MJFF-000858/Michael J. Fox Foundation for Parkinson's Research
- 863214/Horizon 2020 Framework Programme
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

