The complete mitochondrial genomes of five critical phytopathogenic Bipolaris species: features, evolution, and phylogeny
- PMID: 38863028
- PMCID: PMC11167856
- DOI: 10.1186/s43008-024-00149-6
The complete mitochondrial genomes of five critical phytopathogenic Bipolaris species: features, evolution, and phylogeny
Abstract
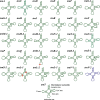
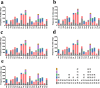
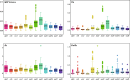
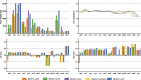
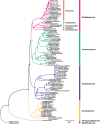
In the present study, three mitogenomes from the Bipolaris genus (Bipolaris maydis, B. zeicola, and B. oryzae) were assembled and compared with the other two reported Bipolaris mitogenomes (B. oryzae and B. sorokiniana). The five mitogenomes were all circular DNA molecules, with lengths ranging from 106,403 bp to 135,790 bp. The mitogenomes of the five Bipolaris species mainly comprised the same set of 13 core protein-coding genes (PCGs), two rRNAs, and a certain number of tRNAs and unidentified open reading frames (ORFs). The PCG length, AT skew and GC skew showed large variability among the 13 PCGs in the five mitogenomes. Across the 13 core PCGs tested, nad6 had the least genetic distance among the 16 Pleosporales species we investigated, indicating that this gene was highly conserved. In addition, the Ka/Ks values for all 12 core PCGs (excluding rps3) were < 1, suggesting that these genes were subject to purifying selection. Comparative mitogenomic analyses indicate that introns were the main factor contributing to the size variation of Bipolaris mitogenomes. The introns of the cox1 gene experienced frequent gain/loss events in Pleosporales species. The gene arrangement and collinearity in the mitogenomes of the five Bipolaris species were almost highly conserved within the genus. Phylogenetic analysis based on combined mitochondrial gene datasets showed that the five Bipolaris species formed well-supported topologies. This study is the first report on the mitogenomes of B. maydis and B. zeicola, as well as the first comparison of mitogenomes among Bipolaris species. The findings of this study will further advance investigations into the population genetics, evolution, and genomics of Bipolaris species.
Keywords: Bipolaris; Comparative analysis; Gene rearrangement; Intron; Mitogenome; Phylogenetic analysis.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures



References
-
- Bankevich A, Nurk S, Antipov D, Gurevich AA, Dvorkin M, Kulikov AS, Lesin VM, Nikolenko SI, Pham S, Prjibelski AD, Pyshkin AV, Sirotkin AV, Vyahhi N, Tesler G, Alekseyev MA, Pevzner PA. SPAdes: a new genome assembly algorithm and its applications to single-cell sequencing. J Comput Biol. 2012;19:455–477. doi: 10.1089/cmb.2012.0021. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
