Herb pair of Huangqi-Danggui exerts anti-tumor immunity to breast cancer by upregulating PIK3R1
- PMID: 38863309
- PMCID: PMC11228089
- DOI: 10.1002/ame2.12434
Herb pair of Huangqi-Danggui exerts anti-tumor immunity to breast cancer by upregulating PIK3R1
Abstract
Background: According to traditional Chinese medicine (TCM), drugs supplementing the vital energy, Qi, can eliminate tumors by restoring host immunity. The objective of this study is to investigate the underlying immune mechanisms of anti-tumor activity associated with Qi-supplementing herbs, specifically the paired use of Huangqi and Danggui.
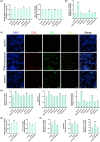
Methods: Analysis of compatibility regularity was conducted to screen the combination of Qi-supplementing TCMs. Using the MTT assay and a transplanted tumor mice model, the anti-tumor effects of combination TCMs were investigated in vitro and in vivo. High content analysis and flow cytometry were then used to evaluate cellular immunity, followed by network pharmacology and molecular docking to dissect the significant active compounds and potential mechanisms. Finally, the anti-tumor activity and the mechanism of the active ingredients were verified by molecular experiments.
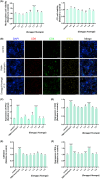
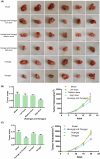
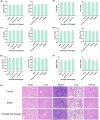
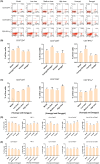
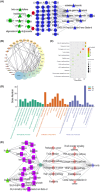
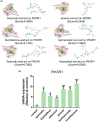
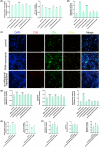
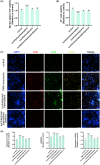
Results: There is an optimal combination of Huangqi and Danggui that, administered as an aqueous extract, can activate immunity to suppress tumor and is more effective than each drug on its own in vitro and in vivo. Based on network pharmacology analysis, PIK3R1 is the core target for the anti-tumor immunity activity of combined Huangqi and Danggui. Molecular docking analysis shows 6 components of the combined Danggui and Huangqi extract (quercetin, jaranol, isorhamnetin, kaempferol, calycosin, and suchilactone) that bind to PIK3R1. Jaranol is the most important component against breast cancer. The suchilactone/jaranol combination and, especially, the suchilactone/kaempferol combination are key for immunity enhancement and the anti-tumor effects of the extract.
Conclusions: The combination of Huangqi and Danggui can activate immunity to suppress breast cancer and is more effective than the individual drugs alone.
Keywords: Danggui; Huangqi; anti‐tumor; immunity.
© 2024 The Author(s). Animal Models and Experimental Medicine published by John Wiley & Sons Australia, Ltd on behalf of The Chinese Association for Laboratory Animal Sciences.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Mechanism of Astragalus membranaceus (Huangqi, HQ) for treatment of heart failure based on network pharmacology and molecular docking.J Cell Mol Med. 2024 May;28(10):e18331. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.18331. J Cell Mol Med. 2024. PMID: 38780500 Free PMC article.
-
Network pharmacology analysis of the Huangqi-Gancao herb pair reveals quercetin as a therapeutics for allergic rhinitis via the RELA-regulated IFNG/IRF1 axis response.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2025 Feb;398(2):1597-1612. doi: 10.1007/s00210-024-03353-8. Epub 2024 Aug 12. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 39133272 Free PMC article.
-
Astragalus injection inhibits the growth of osteosarcoma by activating cytotoxic T lymphocyte and targeting CTSL.J Ethnopharmacol. 2025 Apr 9;345:119607. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2025.119607. Epub 2025 Mar 7. J Ethnopharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40058477
-
Herb pairs containing Angelicae Sinensis Radix (Danggui): A review of bio-active constituents and compatibility effects.J Ethnopharmacol. 2016 Apr 2;181:158-71. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2016.01.033. Epub 2016 Jan 22. J Ethnopharmacol. 2016. PMID: 26807913 Review.
-
An optimized herbal combination for the treatment of liver fibrosis: Hub genes, bioactive ingredients, and molecular mechanisms.J Ethnopharmacol. 2022 Oct 28;297:115567. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2022.115567. Epub 2022 Jul 20. J Ethnopharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35870684 Review.
Cited by
-
Exploring Novel Therapeutic Targets in Breast Cancer via Comprehensive Omics Profiling and Experimental Verification.Biology (Basel). 2025 Apr 11;14(4):405. doi: 10.3390/biology14040405. Biology (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40282270 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Liu Z, Zhao X, Shen H, Liu X, Xu X, Fu R. Cellular immunity in the era of modern multiple myeloma therapy. Int J Cancer. 2023;153:1436‐1447. - PubMed
-
- Chen Y, Li H, Fan Y. Shaping the tumor immune microenvironment of SCLC: mechanisms, and opportunities for immunotherapy. Cancer Treat Rev. 2023;120:102606. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 20210302123310/Natural Science Foundation of Shanxi Province for Youths
- 20210302124668/Natural Science Foundation of Shanxi Province for Youths
- 2022PY-TH-17/Science and technology innovation ability cultivation program project of Shanxi University of Chinese Medicine
- 2022TD1017/The immune regulation Chinese medicine research and development innovation team project
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

