The use of platelet rich plasma in the treatment of degenerative joint disease in cats: an exploratory case series
- PMID: 38863451
- PMCID: PMC11165359
- DOI: 10.3389/fvets.2024.1394055
The use of platelet rich plasma in the treatment of degenerative joint disease in cats: an exploratory case series
Abstract
Objective: To evaluate the effectiveness of intra-articular autologous Platelet Rich Plasma (PRP) in managing Degenerative Joint Disease (DJD) in cats.
Design: Prospective pilot clinical trial.
Methods: Six domestic cats with clinically and radiographically diagnosed DJD received intra-articular injections of autologous PRP. Clinical assessments pre and post intra-articular injections were conducted using the Feline Musculoskeletal Pain Index (FMPI, owner assessed) and Visual Analog Scale (VAS, clinician assessed) at baseline, Day 14, Day 28, and Day 42-45.
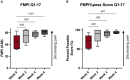
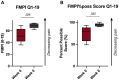
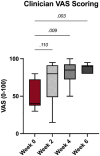
Results: Significant improvements were noted in both FMPI and VAS scores at the end of the study period, indicating enhanced joint function and reduced pain.
Conclusion and clinical relevance: The study suggests the potential of PRP therapy as a safe and effective treatment for feline DJD, warranting further research with larger cohorts and longer follow-up to establish comprehensive treatment guidelines.
Keywords: degenerative joint disease (DJD); feline; osteoarthritis; platelet rich plasma (PRP); regenerative medicine.
Copyright © 2024 Huntingford, Looney, Johnson and Miller.
Conflict of interest statement
JJ and LM are employees of the company who manufactures the CRT PRP system used in this work. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Reliability and discriminatory testing of a client-based metrology instrument, feline musculoskeletal pain index (FMPI) for the evaluation of degenerative joint disease-associated pain in cats.Vet J. 2013 Jun;196(3):368-73. doi: 10.1016/j.tvjl.2012.12.015. Epub 2013 Jan 29. Vet J. 2013. PMID: 23369382
-
Single intra-articular injection with or without intra-osseous injections of platelet-rich plasma in the treatment of osteoarthritis knee: A single-blind, randomized clinical trial.Injury. 2022 Mar;53(3):1247-1253. doi: 10.1016/j.injury.2022.01.012. Epub 2022 Jan 7. Injury. 2022. PMID: 35033356 Clinical Trial.
-
Efficacy of Autologous Platelet-Rich Plasma Injections for Grade 3 Symptomatic Degenerative Meniscal Lesions: A 1-Year Follow-up Prospective Study.Sports Health. 2022 Mar-Apr;14(2):227-236. doi: 10.1177/19417381211011074. Epub 2021 Apr 24. Sports Health. 2022. PMID: 33896253 Free PMC article.
-
The Use of Intra-articular Platelet-Rich Plasma as a Therapeutic Intervention for Hip Osteoarthritis: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis.Am J Sports Med. 2023 Jul;51(9):2487-2497. doi: 10.1177/03635465221095563. Epub 2022 Jun 7. Am J Sports Med. 2023. PMID: 35971803 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative effectiveness of intra-articular therapies in knee osteoarthritis: a meta-analysis comparing platelet-rich plasma (PRP) with other treatment modalities.Ann Med Surg (Lond). 2023 Dec 15;86(1):361-372. doi: 10.1097/MS9.0000000000001615. eCollection 2024 Jan. Ann Med Surg (Lond). 2023. PMID: 38222750 Free PMC article. Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous