Total worker health® based Helicobacter pylori public health prevention strategy
- PMID: 38863480
- PMCID: PMC11163978
- DOI: 10.1097/PXH.0000000000000035
Total worker health® based Helicobacter pylori public health prevention strategy
Abstract
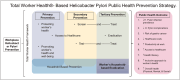
Purpose of review: This review aims to explore the public health approach for Helicobacter pylori Infection Prevention within the Total Worker Health (TWH) framework strategy.
Recent findings: The review identifies certain occupations considered high-risk groups for H. pylori infection. It underscores primary, secondary, and tertiary public health preventive measures align with the TWH approach. Within this framework, the role of raising awareness, emphasizing infection control, worker hygiene, risk assessment, and ensuring healthcare accessibility is emphasized. The importance of early detection, treatment, eradication, and a TWH approach emerges as a central theme. The TWH approach offers a holistic perspective, intertwining occupation-related health risks with overall health and well being.
Summary: Adopting the TWH approach, coupled with household-based infection control and eradication strategies, can significantly reduce H. pylori prevalence, fostering a healthier workforce and diminishing long-term healthcare costs. The review underscores the importance of recognizing H. pylori as an occupational disease. It calls for further research into the "one-health" perspective on H. pylori transmission dynamics.
Keywords: helicobacter pylori; occupational health promotion; public health prevention; total worker health.
Copyright © 2024 The Author(s). Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The Total Worker Health® (TWH) approach: a systematic review of its application in different occupational settings.BMC Public Health. 2024 Jul 30;24(1):2037. doi: 10.1186/s12889-024-19500-y. BMC Public Health. 2024. PMID: 39080673 Free PMC article.
-
Global whole family based-Helicobacter pylori eradication strategy to prevent its related diseases and gastric cancer.World J Gastroenterol. 2020 Mar 14;26(10):995-1004. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v26.i10.995. World J Gastroenterol. 2020. PMID: 32205991 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Total Worker Health Approach to Skin Exposure Assessment: Experiences from the Firefighter Cancer Initiative.Ann Work Expo Health. 2021 Mar 3;65(2):143-147. doi: 10.1093/annweh/wxaa066. Ann Work Expo Health. 2021. PMID: 32618337
-
International Total Worker Health: Applicability to Agribusiness in Latin America.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021 Feb 25;18(5):2252. doi: 10.3390/ijerph18052252. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021. PMID: 33668716 Free PMC article.
-
Epidemiology of Helicobacter pylori infection and public health implications.Helicobacter. 2011 Sep;16 Suppl 1(0 1):1-9. doi: 10.1111/j.1523-5378.2011.00874.x. Helicobacter. 2011. PMID: 21896079 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Marshall BJ, Armstrong JA, McGechie DB, Glancy RJ. Attempt to fulfil Koch's postulates for pyloric Campylobacter. Med J Aust 1985; 142:436–439. - PubMed
-
- Denic M, Touati E, De Reuse H. Review: pathogenesis of Helicobacter pylori infection. Helicobacter 2020; 25: (Suppl 1): e12736. - PubMed
-
- Ražuka-Ebela D, Giupponi B, Franceschi F. Helicobacter pylori and extragastric diseases. Helicobacter 2018; 23:e12520. - PubMed
-
- Gatta L, Nyssen OP, Fiorini G, et al. . Effectiveness of first and second-line empirical treatment in Italy: results of the European registry on Helicobacter pylori management. United European Gastroenterol J 2023; 11:103–113. - PMC - PubMed
-
This article assesses the effectiveness of empirical first and second-line treatments for Helicobacter pylori in Italy, part of the European Registry on H. pylori Management. The findings indicate that quadruple therapies lasting at least 10 days are most effective in achieving over 90% eradication rates, underlining the importance of these treatment regimens in managing H. pylori infection and potentially reducing associated gastric cancer risks.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials